├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Obj Represents a generic policy object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Def Represents self-contained policy document. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
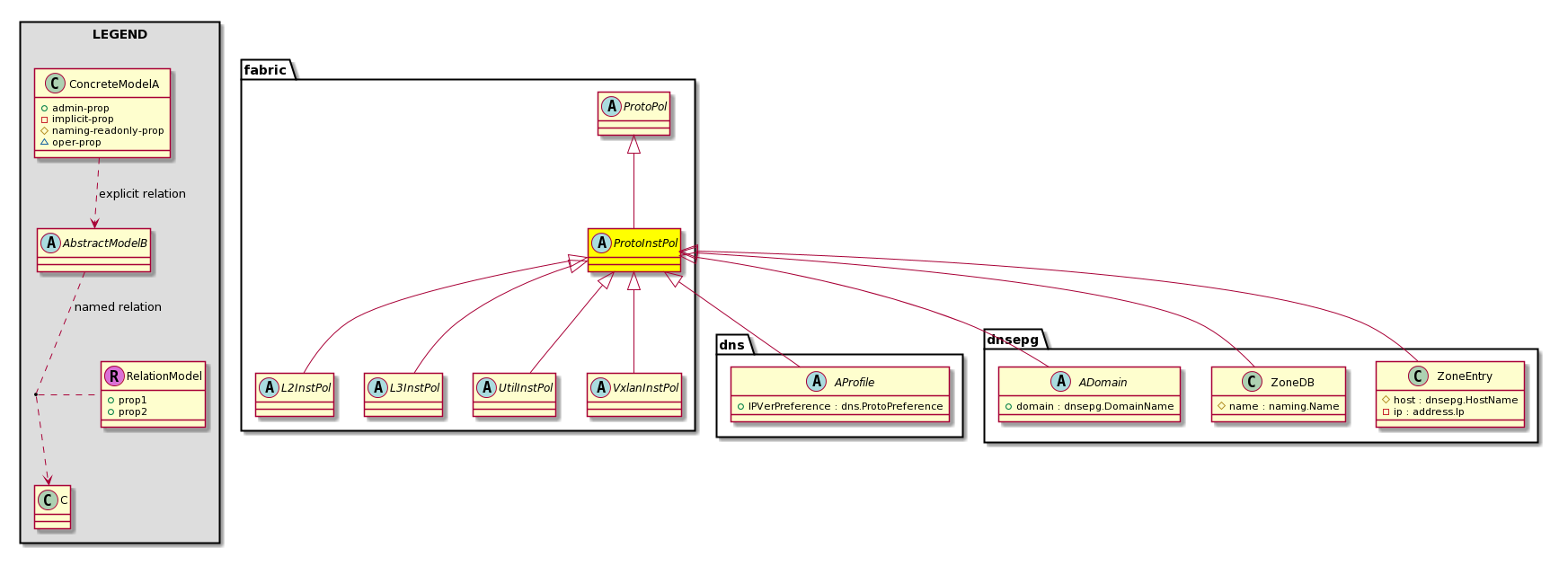
fabric:ProtoInstPol A base class for instance-level protocol policies. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dns:Prof The DNS instance information. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dns:Profile The DNS profile defines a set of DNS providers and can be deployed to a switch for tenant contexts. To deploy a DNS profile on a switch, the appropriate label has to be defined for the context deployed on switch. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
edr:ErrDisRecoverPol The error disabled recovery policy specifies the policy for re-enabling a port that was disabled due to one or more pre-defined error conditions. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ep:LoopProtectP The endpoint loop protection policy specifies how loops detected by frequent mac moves are handled. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l2:InstPol The Layer 2 instance policy is used for configuring fabric-wide layer 2 settings. Currently, this policy contains only fabric MTU and management MTU configuration. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:ADest The abstraction of an SPAN destination. The SPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A SPAN destination can be local or remote (ERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines the allowed types of SPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be either a port or an endpoint group... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:AVDest The abstraction of a VSPAN destination. The VSPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A VSPAN destination can be local or remote (VERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source and a VSPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines the allowed types of VSPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be either a port or an endpoint... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VDest The VSPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A VSPAN destination can be local or remote (VERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source and a VSPAN destination. The type of session (tenant, access, or fabric) determines the allowed types of VSPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be either a port or an endpoint group. If the destination is a port, it... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VDestDef The VLAN-based SPAN (VSPAN) destination definition. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:Dest The SPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A SPAN destination can be local or remote (ERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines the allowed types of SPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be either a port or an endpoint group. If the destination is a port, it shoul... |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:ASrcGrp The abstraction of a SPAN source group. The SPAN source group can contain a group of SPAN sources, which is where network traffic is sampled. A SPAN source can be an endpoint group (EPG), one or more ports, or port traffic filtered by an EPG (Access SPAN), a Layer 2 bridge domain, or a Layer 3 context (Fabric SPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source group and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenan... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:SrcGrp The SPAN source group can contain a group of SPAN sources. A SPAN source is where network traffic is sampled. A SPAN source can be an endpoint group (EPG), one or more ports, or port traffic filtered by an EPG (access SPAN), a Layer 2 bridge domain, or a Layer 3 context (Fabric SPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source group and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:SrcGrpDef The SPAN source group definitions. The SPAN source is where traffic is sampled. A SPAN source can be an endpoint group (EPG), one or more ports, or port traffic filtered by an EPG (access SPAN), a Layer 2 bridge domain, or a Layer 3 context (fabric SPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access or fabric) determines the allowed types of SPAN sources an... |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:AVDestGrp The abstraction of a VSPAN destination group. The VSPAN destination group can contain a group of VSPAN destinations. A VSPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A VSPAN destination can be local or remote (VERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source and a VSPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines the allowed types of VSPAN so... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VDestGrp The VSPAN destination group contains a group of VSPAN destinations. A VSPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A VSPAN destination can be local or remote (VERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source and a VSPAN destination. The type of session (tenant, access, or fabric) determines the allowed types of VSPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be ei... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VDestGrpDef VSPAN destination group used for configuring VSPAN source group definitions. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:AVSrcGrp The abstraction of a VSPAN source group. The VSPAN source group can contain a group of VSPAN sources. A VSPAN source is where network traffic is sampled. A VSPAN source can be an endpoint group (EPG), one or more ports, or port traffic filtered by an EPG (Access VSPAN), a Layer 2 bridge domain, or a Layer 3 context (Fabric VSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source group and a VSPAN destination. The type ... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VSrcGrp The VSPAN source group can contain a group of VSPAN sources. A VSPAN source is where network traffic is sampled. A VSPAN source can be an endpoint group (EPG), one or more ports; or port traffic filtered by an EPG (access VSPAN), a Layer 2 bridge domain, or a Layer 3 context (fabric VSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source group and a VSPAN destination. The type of session (tenant, access, or fabric) de... |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:DestGrp The SPAN destination group contains a group of SPAN destinations. A SPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A SPAN destination can be local or remote (ERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines the allowed types of SPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be either a p... |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:SpanProv The SPAN destination provider is used for configuring SPAN destination provider parameters. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VSpanProv The VSPAN destination provider is used for configuring VSPAN destination provider parameters. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
stp:InstPol The spanning Tree Protocol (STP) instance policy, which enables you to set the bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) guard policy or filter. BDPUs are packets that run the STP protocol. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create loops when you have redundant paths in your network. Loops are deadly to a network. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vpc:InstPol The node-level vPC domain policy, which is used to specify a vPC domain and is applied to both vPC peer devices, the vPC peer keepalive link, the vPC peer link, and all the PortChannels in the vPC domain connected to the downstream device. You can have only one vPC domain ID on each device. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:InstPol The BGP Instance level policy is used to configure MP-BGP policies inside the fabric. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:ARelayP The abstract DHCP Relay profile, which is used for configuring relay parameters per bridge domain (BD). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:RelayP The DHCP relay profile, with one or more helper addresses in it, configures a DHCP relay agent for forwarding DHCP packets to a remote server. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
psu:InstPol The power redundancy policy is for all power supply units on the fabric nodes (leaves and spines) that are consuming the power supply policy through their respective selector profile policy. |
|