├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
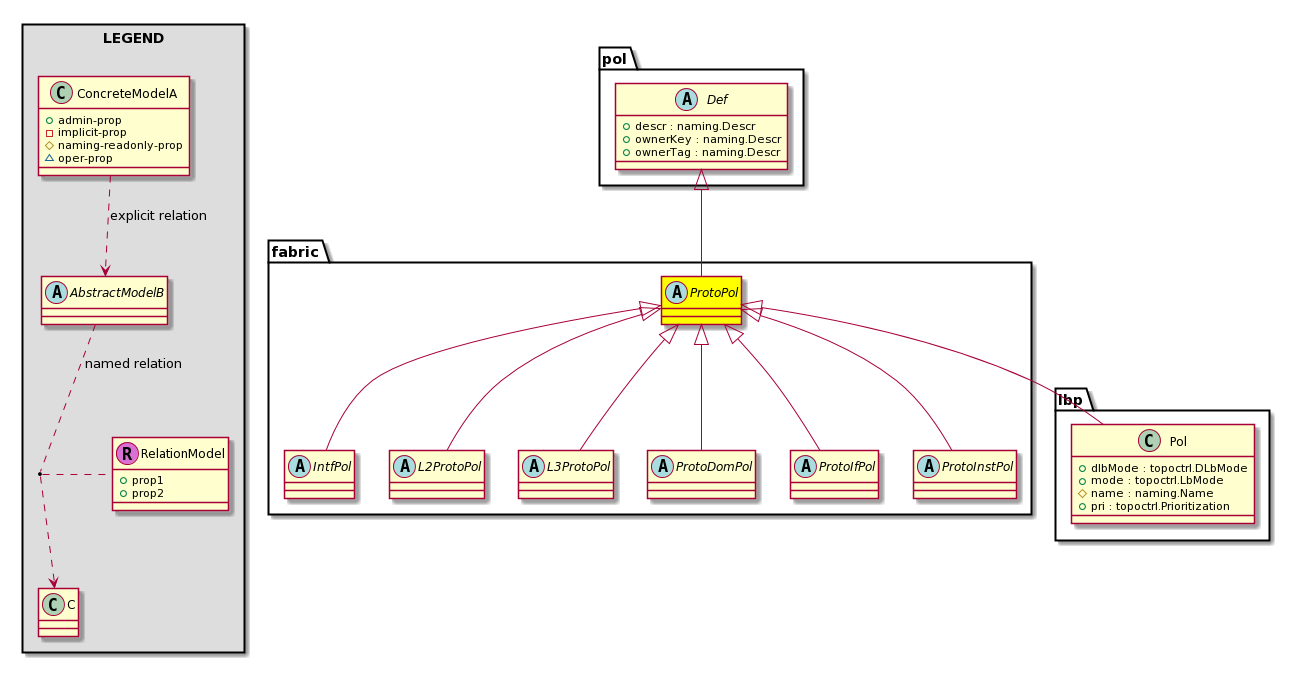
pol:Obj Represents a generic policy object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Def Represents self-contained policy document. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fabric:ProtoPol A base class for protocol policies. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fabric:HIfPol The host interface policy specifies the layer 1 parameters of host facing ports. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:PeerPfxPol The peer prefix policy defines how many prefixes can be received from a neighbor and the action to take when the number of allowed prefixes is exceeded. This feature is commonly used for external BGP peers, but can also be applied to internal BGP peers. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
coop:Pol The COOP policy contains groups of Oracles nodes and COOP repositories. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EpRetPol The endpoint retention policy provides the parameters for the lifecycle of the endpoints. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
igmp:ASnoopPol Restricts flooding of multicast traffic by sending multicast traffic only to the bridge domains that are subscribed to a particular multicast group. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
igmp:SnoopDef The process of listening to Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) network traffic. The feature allows a network switch to listen in on the IGMP conversation between hosts and routers. By listening to these conversations the switch maintains a map of which links need which IP multicast streams. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
igmp:SnoopPol The IGMP snooping policy streamlines multicast traffic handling for VLANs. By examining (snooping) IGMP membership report messages from interested hosts, multicast traffic is limited to the subset of VLAN interfaces on which the hosts reside. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:CtxDef An internal object for the BGP context-level policy definition. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:CtxPol The BGP timers policy uses timers to control periodic activities such as the frequency keepalive messages that are sent to its peer, the amount of time the system waits to declare a peer dead after keepalive messages stop being received, and the amount of time before restarting a dead peer. The BGP timer policy enables you to specify the intervals for the periodic activities and supplies two options for graceful restart control: the graceful rest... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
eigrp:ACtxAfPol The abstraction of the context-level EIGRP policy, which contains the configuration for an address family on a context on the node. The EIGRP policy is configured under the tenant protocol policies and can be applied to one or more contexts (private domains) under the tenant. The EIGRP context policy can be enabled on a context through a relation in the context per address family. If there is no relation to a given address family, or the EIGRP c... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
eigrp:CtxAfPol An EIGRP context policy can be applied on one or more contexts under the tenant. EIGRP context policies can be enabled on a context through a relation in the context per address family. If there is no relation to a given address family such as IPv6 or the EIGRP context policy mentioned in the relation doesn't exist, then the default context policy created under Tenant Common will be used for that address family. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ipmc:ACtxPol Abstraction of Context-level Routed Multicast policy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:CtxDefAf The context-level OSPF definition per address family. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:CtxPol The context-level OSPF timer policy provides the Hello timer and Dead timer intervals configuration. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
rtdmc:ACtxPol Abstraction of Context-level Routed Multicast policy |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
isis:DomPol The domain policy is used to configure IS-IS domain specific properties. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
stormctrl:IfPol The storm control interface policy. A traffic storm occurs when packets flood the LAN, creating excessive traffic and degrading network performance. You can use the traffic storm control feature to prevent disruptions on ports by a broadcast, multicast, or unknown unicast traffic storm on physical interfaces. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
cdp:AIfPol The CDP Interface Policy parameters. CDP is primarily used to obtain protocol addresses of neighboring devices and discover the platform of those devices. CDP can also be used to display information about the interfaces your router uses. CDP is media- and protocol-independent, and runs on all Cisco-manufactured equipment including routers, bridges, access servers, and switches. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
cdp:IfPol The CDP interface policy, which is primarily used to obtain protocol addresses of neighboring devices and discover the platform of those devices. CDP can also be used to display information about the interfaces your router uses. CDP is media- and protocol-independent, and runs on all Cisco-manufactured equipment including routers, bridges, access servers, and switches. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
copp:IfPol Per interface per protocol CoPP policy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lacp:LagPol The PortChannel policy enables you to bundle several physical ports together to form a single port channel. LACP enables a node to negotiate an automatic bundling of links by sending LACP packets to the peer node. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lacp:IfPol The PortChannel interface policy defines a common configuration that will apply to one or more LACP interfaces. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:AIfPol A summary of the interface policy. We recommend you include information about where and when the policy should be used. The abstraction can be up to 128 characters. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:IfPol The LLDP interface policy, which defines a common configuration that will apply to one or more LLDP interfaces. LLDP uses the logical link control (LLC) services to transmit and receive information to and from other LLDP agents. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
netflow:ExporterPolDef Define the Netflow Exporter Policy MO which contains
internal information needed to program the leaf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
netflow:MonitorPolDef Define the Netflow Monitor Policy MO which contains
internal information needed to program the leaf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
netflow:RecordPolDef Define the Netflow Record Policy MO which contains
internal information needed to program the leaf |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
qos:ADppPol Define a Data Plane Policing policy. User is supposed
to use this in scenarios where the incoming traffic need
to be policed to certain levels |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
qos:DppPol Define a Data Plane Policing policy. User is supposed
to use this in scenarios where the incoming traffic need
to be policed to certain levels |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
qos:DppPolDef Define the Data Plane Policing MO which contains
internal information needed to program the leaf |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
stp:AIfPol An abstraction of an spanning-tree protocol interface policy. This is applicable to leaf ports and n1000v distributed virtual switches. Extended chassis ports have BPDU guard filter enabled by default. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
stp:IfPol The Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) interface policy defines a common configuration that will apply to one or more interfaces.
STP prevents loops from being formed when the interfaces are interconnected via multiple paths. Spanning-Tree Protocol implements the 802.1D IEEE algorithm by exchanging BPDU messages with other switches to detect loops, and then removes the loop by shutting down selected bridge interfaces. This algorithm guarantees that th... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
stp:IfPolDef The read-only copy of the spanning-tree protocol interface policy. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bfd:AIfPol Interface-level bfd abstraction policy |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
eigrp:IfPol The EIGRP interface policy, which defines a common configuration that will apply to one or more EIGRP interfaces. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
nd:AIfPol The neighbor discovery interface policy defines a common configuration that will apply to one or more neighbor discovery interfaces. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
nd:IfPol The neighbor discovery interface policy defines a common configuration that will apply to one or more neighbor discovery interfaces. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
nd:IfPolDef The read only copy of the neighbor discovery interface policy. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
nd:APfxPol The neighbor discovery prefix policy. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
nd:PfxPol The neighbor discovery prefix policy. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
nd:PfxPolDef The neighbor discovery prefix policy definition. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:IfPol The OSPF interface-level policy information. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pim:IfPol Interface-level PIM-SM (sparse mode) policy. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dns:Prof The DNS instance information. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dns:Profile The DNS profile defines a set of DNS providers and can be deployed to a switch for tenant contexts. To deploy a DNS profile on a switch, the appropriate label has to be defined for the context deployed on switch. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
edr:ErrDisRecoverPol The error disabled recovery policy specifies the policy for re-enabling a port that was disabled due to one or more pre-defined error conditions. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ep:LoopProtectP The endpoint loop protection policy specifies how loops detected by frequent mac moves are handled. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l2:InstPol The Layer 2 instance policy is used for configuring fabric-wide layer 2 settings. Currently, this policy contains only fabric MTU and management MTU configuration. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:ADest The abstraction of an SPAN destination. The SPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A SPAN destination can be local or remote (ERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines the allowed types of SPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be either a port or an endpoint group... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:AVDest The abstraction of a VSPAN destination. The VSPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A VSPAN destination can be local or remote (VERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source and a VSPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines the allowed types of VSPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be either a port or an endpoint... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VDest The VSPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A VSPAN destination can be local or remote (VERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source and a VSPAN destination. The type of session (tenant, access, or fabric) determines the allowed types of VSPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be either a port or an endpoint group. If the destination is a port, it... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VDestDef The VLAN-based SPAN (VSPAN) destination definition. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:Dest The SPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A SPAN destination can be local or remote (ERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines the allowed types of SPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be either a port or an endpoint group. If the destination is a port, it shoul... |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:ASrcGrp The abstraction of a SPAN source group. The SPAN source group can contain a group of SPAN sources, which is where network traffic is sampled. A SPAN source can be an endpoint group (EPG), one or more ports, or port traffic filtered by an EPG (Access SPAN), a Layer 2 bridge domain, or a Layer 3 context (Fabric SPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source group and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenan... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:SrcGrp The SPAN source group can contain a group of SPAN sources. A SPAN source is where network traffic is sampled. A SPAN source can be an endpoint group (EPG), one or more ports, or port traffic filtered by an EPG (access SPAN), a Layer 2 bridge domain, or a Layer 3 context (Fabric SPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source group and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:SrcGrpDef The SPAN source group definitions. The SPAN source is where traffic is sampled. A SPAN source can be an endpoint group (EPG), one or more ports, or port traffic filtered by an EPG (access SPAN), a Layer 2 bridge domain, or a Layer 3 context (fabric SPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access or fabric) determines the allowed types of SPAN sources an... |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:AVDestGrp The abstraction of a VSPAN destination group. The VSPAN destination group can contain a group of VSPAN destinations. A VSPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A VSPAN destination can be local or remote (VERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source and a VSPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines the allowed types of VSPAN so... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VDestGrp The VSPAN destination group contains a group of VSPAN destinations. A VSPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A VSPAN destination can be local or remote (VERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source and a VSPAN destination. The type of session (tenant, access, or fabric) determines the allowed types of VSPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be ei... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VDestGrpDef VSPAN destination group used for configuring VSPAN source group definitions. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:AVSrcGrp The abstraction of a VSPAN source group. The VSPAN source group can contain a group of VSPAN sources. A VSPAN source is where network traffic is sampled. A VSPAN source can be an endpoint group (EPG), one or more ports, or port traffic filtered by an EPG (Access VSPAN), a Layer 2 bridge domain, or a Layer 3 context (Fabric VSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source group and a VSPAN destination. The type ... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VSrcGrp The VSPAN source group can contain a group of VSPAN sources. A VSPAN source is where network traffic is sampled. A VSPAN source can be an endpoint group (EPG), one or more ports; or port traffic filtered by an EPG (access VSPAN), a Layer 2 bridge domain, or a Layer 3 context (fabric VSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a VSPAN source group and a VSPAN destination. The type of session (tenant, access, or fabric) de... |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:DestGrp The SPAN destination group contains a group of SPAN destinations. A SPAN destination is where network traffic is sent for analysis by a network analyzer. A SPAN destination can be local or remote (ERSPAN). When you create a traffic monitoring session, you must select a SPAN source and a SPAN destination. The type of session (Tenant, Access, or Fabric) determines the allowed types of SPAN sources and destinations. The destination can be either a p... |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:SpanProv The SPAN destination provider is used for configuring SPAN destination provider parameters. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
span:VSpanProv The VSPAN destination provider is used for configuring VSPAN destination provider parameters. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
stp:InstPol The spanning Tree Protocol (STP) instance policy, which enables you to set the bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) guard policy or filter. BDPUs are packets that run the STP protocol. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create loops when you have redundant paths in your network. Loops are deadly to a network. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vpc:InstPol The node-level vPC domain policy, which is used to specify a vPC domain and is applied to both vPC peer devices, the vPC peer keepalive link, the vPC peer link, and all the PortChannels in the vPC domain connected to the downstream device. You can have only one vPC domain ID on each device. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:InstPol The BGP Instance level policy is used to configure MP-BGP policies inside the fabric. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:ARelayP The abstract DHCP Relay profile, which is used for configuring relay parameters per bridge domain (BD). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:RelayP The DHCP relay profile, with one or more helper addresses in it, configures a DHCP relay agent for forwarding DHCP packets to a remote server. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
psu:InstPol The power redundancy policy is for all power supply units on the fabric nodes (leaves and spines) that are consuming the power supply policy through their respective selector profile policy. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lbp:Pol The load balancing policy options for balancing traffic among the available uplink ports. Static hash load balancing is the traditional load balancing mechanism used in networks where each flow is allocated to an uplink based on a hash of its 5-tuple. This load balancing gives a distribution of flows across the available links that is roughly even. Usually, with a large number of flows, the even distribution of flows results in an even distributi... |
|