![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
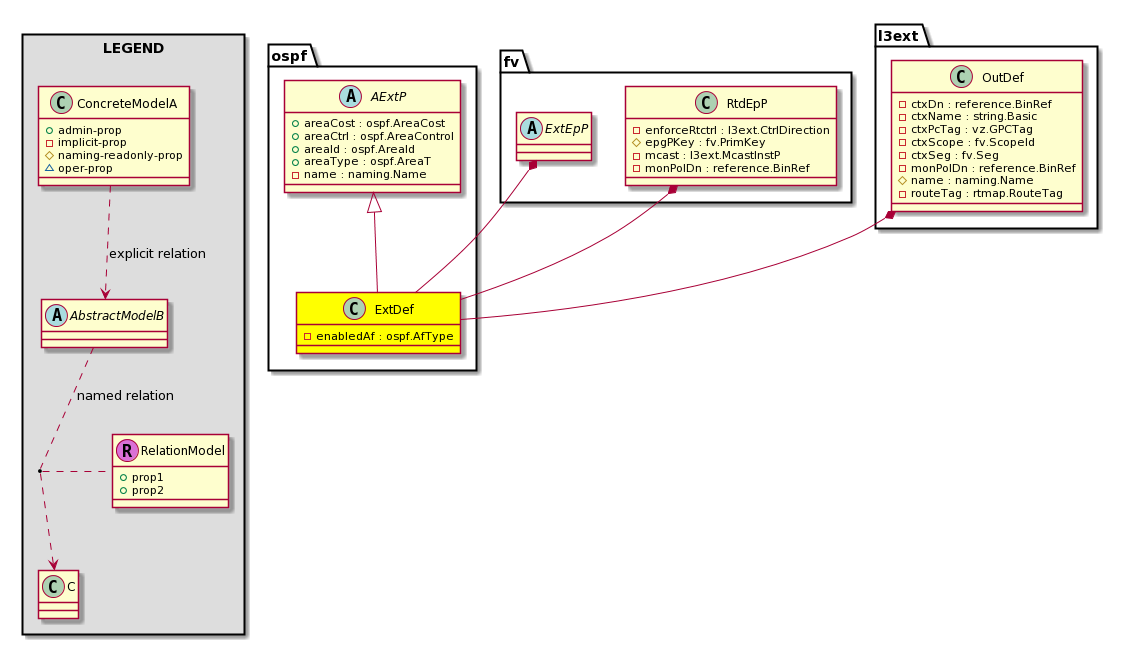
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:IpToIp IP Addr to IP policy Defn. Used for an
external host identified by its IP address to
another IP address
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:IpToIp IP Addr to IP policy Defn. Used for an
external host identified by its IP address to
another IP address
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:ExtToEp The external host-to-endpoint atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:ExtToEp The external host-to-endpoint atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpToExt The endpoint-to-external IP address atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpToExt The endpoint-to-external IP address atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpToEp The endpoint-to-endpoint atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpToEp The endpoint-to-endpoint atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:AnyToEp Atomic counters detect drops and misrouting in the fabric enables quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:AnyToEp Atomic counters detect drops and misrouting in the fabric enables quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpToAny The endpoint-to-any atomic counter policy which detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpToAny The endpoint-to-any atomic counter policy which detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpgToEp The endpoint group-to-endpoint atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpgToEp The endpoint group-to-endpoint atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpToEpg The endpoint-to-endpoint group atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpToEpg The endpoint-to-endpoint group atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:IpToEpg The IP-to-endpoint group atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric and enables quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:IpToEpg The IP-to-endpoint group atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric and enables quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpgToIp The endpoint group-to-IP atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpgToIp The endpoint group-to-IP atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpgToEpg The endpoint group-to-endpoint group atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:EpgToEpg The endpoint group-to-endpoint group atomic counter policy detects drops and misrouting in the fabric to enable quick debugging and isolation of application connectivity issues. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EpPCont The container for an endpoint profile. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:TenantSpaceCmnDef The tenant space common definition. This atomic counter managed object is used internally for managing Epg/Epp source
and destination policies. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EpPCont The container for an endpoint profile. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dbgac:TenantSpaceCmnDef The tenant space common definition. This atomic counter managed object is used internally for managing Epg/Epp source
and destination policies. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:LDevCtx A device cluster context points to the device cluster used to pick a specific device based on contract, subject, and function label or names. To specify a wild card, set the name to Any. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:LIfCtx The logical interface context points to the logical interface used to pick a specific logical interface based on the connector name. To specify a wild card, set the name to Any. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:LDevCtx A device cluster context points to the device cluster used to pick a specific device based on contract, subject, and function label or names. To specify a wild card, set the name to Any. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:LIfCtx The logical interface context points to the logical interface used to pick a specific logical interface based on the connector name. To specify a wild card, set the name to Any. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Tenant A policy owner in the virtual fabric. A tenant can be either a private or a shared entity. For example, you can create a tenant with contexts and bridge domains shared by other tenants. A shared type of tenant is typically named common, default, or infra. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EpPCont The container for an endpoint profile. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtdEpP A target relation to an L3 routed outside present under a tenant. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EpPCont The container for an endpoint profile. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtdEpP A target relation to an L3 routed outside present under a tenant. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EpPCont The container for an endpoint profile. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:BrEpP The bridge endpoint profile represents L2 outside present under a tenant. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EpPCont The container for an endpoint profile. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:BrEpP The bridge endpoint profile represents L2 outside present under a tenant. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EpPCont The container for an endpoint profile. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ExtEpP Abstraction of a profile created for an endpoint connected to an external router or switch. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pol:Uni Represents policy definition/resolution universe. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EpPCont The container for an endpoint profile. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ExtEpP Abstraction of a profile created for an endpoint connected to an external router or switch. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ospf:ExtDef The external definition profile. |
|