![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
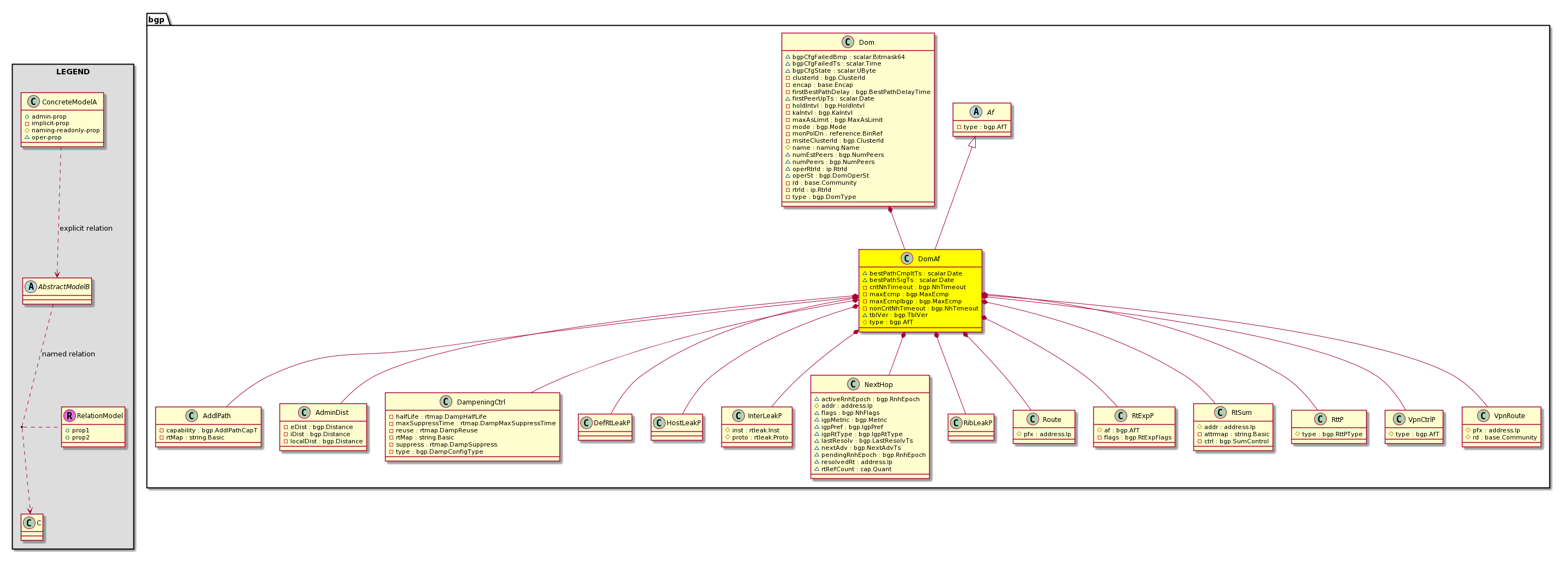
bgp:DomAf The BGP (VRF) address family information. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:AddlPath BGP Additional Paths feature allows the advertisement of multiple
paths through the same peering session for the same prefix without
the new paths implicitly replacing any previous paths |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:AdminDist The administrative distance is used by routers to select the best path when there are two or more different routes to the same destination from two different routing protocols. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:HostLeakP COOP/L2RIB to BGP host route leak policy. This defines
policy to control the distribution of host routes from
COOP/L2RIB to BGP |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:InterLeakP A policy that defines distribution of routes from one protocol to another protocol. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:NextHop The BGP route information for the next hop. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:Route The BGP route table for a particular address family (IPv4 unicast and IPv6 unicast), which contains all the routes advertised by peers and also redistributed into BGP from other routing protocols. This route table is per tenant context (per VRF). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:AsSeg The BGP path AS segment information. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:RtExpP Route export policy to control whether to export routes
into a different address family. Destination address
family is specified in the object.
Object may be nested within peer Address family (AF) to
subject only those peer's particular AF routes to export.
Object can also be under a domain Address family in
which case it is applicable to all pe... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:RtCtrlMapP Route control map policy for routes imported/exported
into an AF. Control is through route maps. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:VpnCtrlP This object holds policy to control vpn af
information for a given vrf |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:PfxLeakCtrlP This object holds route control policy for all networks
defined by PfxLeakP in that domain |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:PfxLeakP This objects holds route leak policy for a given network |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ip:Cons Used for maintaining consumers of a static route from an IPRoueDef. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:RtP Route policy holds all route targets and route controls |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:RtCtrlMapP Route control map policy for routes imported/exported
into an AF. Control is through route maps. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:VpnRoute The BGP route table for a VPN address family (VPNv4 unicast and VPNv6 unicast). The VPN address family routes are exchanged within the fabric over MP-BGP sessions between spines and leafs. Routes are advertised from border leafs to non-border leafs with spines acting as route reflectors. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
bgp:AsSeg The BGP path AS segment information. |
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif)