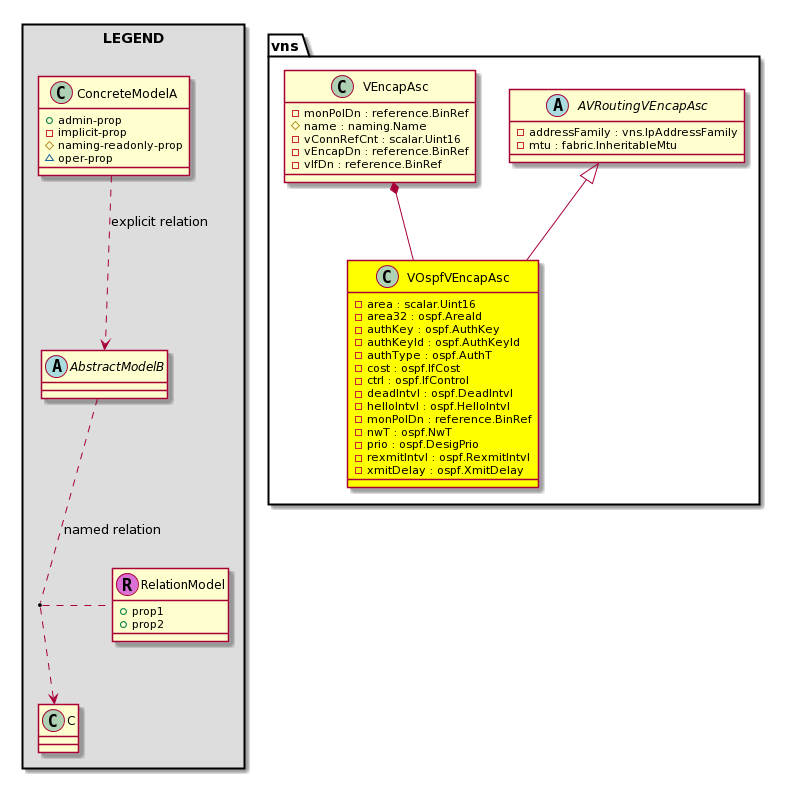
| Properties Summary |
| Defined in: vns:VOspfVEncapAsc |
|
scalar:Uint16
|
area (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:area)
The OSPF Area ID. An area is a logical collection of OSPF networks, routers, and links that have the same area identification. A router within an area must maintain a topological database for the area to which it belongs. The router doesn't have detailed information about network topology outside of its area, thereby reducing the size of its database. Areas limit the scope of route information distribution. It is not possible to do route update filtering within an area. The link-state database (LSDB) of routers within the same area must be synchronized and be exactly the same; however, route summarization and filtering is possible between different areas. The main benefit of creating areas is a reduction in the number of routes to propagate—by the filtering and the summarization of routes. Areas are identified by an area ID. Cisco IOS software supports area IDs expressed in IP address format or decimal format, for example, area 0.0.0.0 is equal to area 0.
|
ospf:AreaId
address:IPv4
|
area32 (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:area32)
NO COMMENTS
|
ospf:AuthKey
string:Password
|
authKey (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:authKey)
The OSPF authentication key specifier.
|
ospf:AuthKeyId
scalar:UByte
|
authKeyId (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:authKeyId)
The authentication key ID.
|
ospf:AuthT
scalar:Enum8
|
authType (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:authType)
The OSPF authentication type specifier. The type options are; default, md5, none, and simple.
|
ospf:IfCost
scalar:Uint16
|
cost (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:cost)
The OSPF Area cost for the default summary LSAs. The Area cost is used with NSSA and stub area types only.
|
ospf:IfControl
scalar:Bitmask8
|
ctrl (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:ctrl)
The control state.
|
ospf:DeadIntvl
scalar:Uint16
|
deadIntvl (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:deadIntvl)
The interval between hello packets from a neighbor before the router declares the neighbor as down. This value must be the same for all networking devices on a specific network. Specifying a smaller dead interval (seconds) will give faster detection of a neighbor being down and improve convergence, but might cause more routing instability.
|
ospf:HelloIntvl
scalar:Uint16
|
helloIntvl (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:helloIntvl)
The hello interval.
|
|
reference:BinRef
|
monPolDn (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:monPolDn)
The monitoring policy attached to this observable object.
|
ospf:NwT
scalar:Enum8
|
nwT (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:nwT)
The OSPF interface policy network type. OSPF supports point-to-point and broadcast.
|
ospf:DesigPrio
scalar:UByte
|
prio (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:prio)
The QoS priority class ID.
|
ospf:RexmitIntvl
scalar:Uint16
|
rexmitIntvl (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:rexmitIntvl)
The interval between LSA retransmissions. The retransmit interval occurs while the router is waiting for an acknowledgement from the neighbor router that it received the LSA. If no acknowlegment is received at the end of the interval, then the LSA is resent.
|
ospf:XmitDelay
scalar:Uint16
|
xmitDelay (vns:VOspfVEncapAsc:xmitDelay)
The delay time needed to send an LSA update packet. OSPF increments the LSA age time by the transmit delay amount before transmitting the LSA update. You should take into account the transmission and propagation delays for the interface when you set this value.
|
| Defined in: vns:AL4L7ServiceFault |
|
scalar:Uint32
|
faultCode (vns:AL4L7ServiceFault:faultCode)
The code corresponding to a service fault. The code characterizes information about the fault. The fault may be reported while updating a configuration or polling for health or counter values.
|
|
string:Basic
|
faultMessage (vns:AL4L7ServiceFault:faultMessage)
The message returned with a service fault. The message provides descriptive information about the fault. The fault may be reported while updating a configuration or polling for health or counter values.
|
condition:Severity
scalar:Enum8
|
faultSeverity (vns:AL4L7ServiceFault:faultSeverity)
The severity of a service fault. The fault may be reported while updating a configuration or polling for health or counter values.
|
| Defined in: mo:Resolvable |
mo:Owner
scalar:Enum8
|
lcOwn (mo:Resolvable:lcOwn)
A value that indicates how this object was created. For internal use only.
|
addressFamily
Type: vns:IpAddressFamily
Primitive Type: scalar:Bitmask8
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
| |
| Constants |
| ipv4 |
1 |
IPv4 |
NO COMMENTS
|
| ipv6 |
2 |
IPv6 |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
0 |
--- |
Bitmap of supported IP address families
|
|
area
Type: scalar:Uint16
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The OSPF Area ID. An area is a logical collection of OSPF networks, routers, and links that have the same area identification. A router within an area must maintain a topological database for the area to which it belongs. The router doesn't have detailed information about network topology outside of its area, thereby reducing the size of its database. Areas limit the scope of route information distribution. It is not possible to do route update filtering within an area. The link-state database (LSDB) of routers within the same area must be synchronized and be exactly the same; however, route summarization and filtering is possible between different areas. The main benefit of creating areas is a reduction in the number of routes to propagate—by the filtering and the summarization of routes. Areas are identified by an area ID. Cisco IOS software supports area IDs expressed in IP address format or decimal format, for example, area 0.0.0.0 is equal to area 0.
area32
Type: ospf:AreaId
Primitive Type: address:IPv4
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
NO COMMENTS
| |
| Constants |
| backbone |
0u |
Backbone area |
NO COMMENTS
|
| defaultValue |
1u |
--- |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
authKey
Type: ospf:AuthKey
Primitive Type: string:Password
Like: ospf:AIfP:authKey
Units: null
Encrypted: true
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The OSPF authentication key specifier.
authKeyId
Type: ospf:AuthKeyId
Primitive Type: scalar:UByte
Like: ospf:AIfP:authKeyId
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The authentication key ID.
| |
| Constants |
| defaultValue |
1 |
--- |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
authType
Type: ospf:AuthT
Primitive Type: scalar:Enum8
Like: ospf:AIfP:authType
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The OSPF authentication type specifier. The type options are; default, md5, none, and simple.
| |
| Constants |
| none |
0 |
No authentication |
None
|
| simple |
1 |
Simple authentication |
Simple
|
| md5 |
2 |
MD5 authentication |
MD5
|
| DEFAULT |
none(0) |
No authentication |
None
|
|
childAction
Type: mo:ModificationChildAction
Primitive Type: scalar:Bitmask32
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelChildAction
Comments:
-
Delete or ignore. For internal use only.
| |
| Constants |
| deleteAll |
16384u |
deleteAll |
NO COMMENTS
|
| ignore |
4096u |
ignore |
NO COMMENTS
|
| deleteNonPresent |
8192u |
deleteNonPresent |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
0 |
--- |
This type is used to
|
|
cost
Type: ospf:IfCost
Primitive Type: scalar:Uint16
Like: ospf:AIf:cost
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The OSPF Area cost for the default summary LSAs. The Area cost is used with NSSA and stub area types only.
| |
| Constants |
| unspecified |
0 |
Unspecified |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
unspecified(0) |
Unspecified |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
ctrl
Type: ospf:IfControl
Primitive Type: scalar:Bitmask8
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The control state.
| |
| Constants |
| unspecified |
0 |
Unspecified |
Unspecified
|
| passive |
1 |
Passive participation |
Passive, the interface doesn't participate in OSPF
protocol and will not establish adjacencies or send
routing updates. However the interface is announced
as part of the routing network
|
| mtu-ignore |
2 |
MTU ignore |
MTU ignore, disables MTU mismatch detection on an
interface.
|
| advert-subnet |
4 |
Advertise subnet |
Advertise ip subnet instead of a host mask in the
router LSA
|
| bfd |
8 |
BFD |
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
|
| DEFAULT |
unspecified(0) |
Unspecified |
Unspecified
|
|
deadIntvl
Type: ospf:DeadIntvl
Primitive Type: scalar:Uint16
Like: ospf:AIf:deadIntvl
Units: sec
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The interval between hello packets from a neighbor before the router declares the neighbor as down. This value must be the same for all networking devices on a specific network. Specifying a smaller dead interval (seconds) will give faster detection of a neighbor being down and improve convergence, but might cause more routing instability.
| |
| Constants |
| defaultValue |
40 |
--- |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
dn
Type: reference:BinRef
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelDn
Comments:
-
A tag or metadata is a non-hierarchical keyword or term assigned to the fabric module.
faultCode
Type: scalar:Uint32
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: oper
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The code corresponding to a service fault. The code characterizes information about the fault. The fault may be reported while updating a configuration or polling for health or counter values.
faultMessage
Type: string:Basic
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: oper
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The message returned with a service fault. The message provides descriptive information about the fault. The fault may be reported while updating a configuration or polling for health or counter values.
faultSeverity
Type: condition:Severity
Primitive Type: scalar:Enum8
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: oper
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The severity of a service fault. The fault may be reported while updating a configuration or polling for health or counter values.
| |
| Constants |
| cleared |
0 |
cleared |
The Cleared severity level indicates the clearing of one or more previously reported alarms. This
alarm clears all alarms for this managed object that have the same Alarm type, Probable cause and
Specific problems (if given). Multiple associated notifications may be cleared by using the Correlated
notifications parameter (defined below).
|
| info |
1 |
info |
NO COMMENTS
|
| warning |
2 |
warning |
The Warning severity level indicates the detection of a potential or impending service affecting
fault, before any significant effects have been felt. Action should be taken to further diagnose (if
necessary) and correct the problem in order to prevent it from becoming a more serious service affecting
fault.
|
| minor |
3 |
minor |
The Minor severity level indicates the existence of a non-service affecting fault condition and that
corrective action should be taken in order to prevent a more serious (for example, service affecting) fault.
Such a severity can be reported, for example, when the detected alarm condition is not currently
degrading the capacity of the managed object.
|
| major |
4 |
major |
The Major severity level indicates that a service affecting condition has developed and an urgent
corrective action is required. Such a severity can be reported, for example, when there is a severe
degradation in the capability of the managed object and its full capability must be restored.
|
| critical |
5 |
critical |
The Critical severity level indicates that a service affecting condition has occurred and an
immediate corrective action is required. Such a severity can be reported, for example, when a managed
object becomes totally out of service and its capability must be restored.
|
| DEFAULT |
minor(3) |
minor |
The Minor severity level indicates the existence of a non-service affecting fault condition and that
corrective action should be taken in order to prevent a more serious (for example, service affecting) fault.
Such a severity can be reported, for example, when the detected alarm condition is not currently
degrading the capacity of the managed object.
|
|
helloIntvl
Type: ospf:HelloIntvl
Primitive Type: scalar:Uint16
Like: ospf:AIf:helloIntvl
Units: sec
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The hello interval.
| |
| Constants |
| defaultValue |
10 |
--- |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
lcOwn
Type: mo:Owner
Primitive Type: scalar:Enum8
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
A value that indicates how this object was created. For internal use only.
| |
| Constants |
| local |
0 |
Local |
NO COMMENTS
|
| policy |
1 |
Policy |
NO COMMENTS
|
| replica |
2 |
Replica |
NO COMMENTS
|
| resolveOnBehalf |
3 |
ResolvedOnBehalf |
NO COMMENTS
|
| implicit |
4 |
Implicit |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
local(0) |
Local |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
modTs
Type: mo:TStamp
Primitive Type: scalar:Date
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The time when this object was last modified.
| |
| Constants |
| never |
0ull |
never |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
never(0ull) |
never |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
monPolDn
Type: reference:BinRef
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The monitoring policy attached to this observable object.
mtu
Type: fabric:InheritableMtu
Primitive Type: scalar:Uint32
Units: bytes
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The administrative MTU port on the aggregated interface.
| |
| Constants |
| inherit |
1u |
inherit |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
inherit(1u) |
inherit |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
name
Type: naming:Name
Primitive Type: string:Basic
Like: naming:Named:name
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: admin
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The name of the object.
nameAlias
Type: naming:NameAlias
Primitive Type: string:Basic
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: admin
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
NO COMMENTS
nwT
Type: ospf:NwT
Primitive Type: scalar:Enum8
Like: ospf:AIf:nwT
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The OSPF interface policy network type. OSPF supports point-to-point and broadcast.
| |
| Constants |
| unspecified |
0 |
Unspecified |
Unspecified
|
| p2p |
1 |
Point-to-point |
p2p interface
|
| bcast |
2 |
Broadcast |
Broadcast interface
|
| DEFAULT |
unspecified(0) |
Unspecified |
Unspecified
|
|
prio
Type: ospf:DesigPrio
Primitive Type: scalar:UByte
Like: ospf:AIf:prio
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The QoS priority class ID.
| |
| Constants |
| defaultValue |
1 |
--- |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
rexmitIntvl
Type: ospf:RexmitIntvl
Primitive Type: scalar:Uint16
Like: ospf:AIf:rexmitIntvl
Units: sec
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The interval between LSA retransmissions. The retransmit interval occurs while the router is waiting for an acknowledgement from the neighbor router that it received the LSA. If no acknowlegment is received at the end of the interval, then the LSA is resent.
| |
| Constants |
| defaultValue |
5 |
--- |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
rn
Type: reference:BinRN
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRn
Comments:
-
Identifies an object from its siblings within the context of its parent object. The distinguished name contains a sequence of relative names.
status
Type: mo:ModificationStatus
Primitive Type: scalar:Bitmask32
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelStatus
Comments:
-
The upgrade status. This property is for internal use only.
| |
| Constants |
| created |
2u |
created |
In a setter method: specifies that an object should be created.
An error is returned if the object already exists.
In the return value of a setter method: indicates that an object has been created.
|
| modified |
4u |
modified |
In a setter method: specifies that an object should be modified
In the return value of a setter method: indicates that an object has been modified.
|
| deleted |
8u |
deleted |
In a setter method: specifies that an object should be deleted.
In the return value of a setter method: indicates that an object has been deleted.
|
| DEFAULT |
0 |
--- |
This type controls the life cycle of objects passed in the XML API.
When used in a setter method (such as configConfMo), the ModificationStatus
specifies whether an object should be created, modified, deleted or removed.
In the return value of a setter method, the ModificationStatus indicates the actual
operation that was performed. For example, the ModificationStatus is set to "created"
if the object was created. The ModificationStatus is not set if the object was neither
created, modified, deleted or removed.
When invoking a setter method, the ModificationStatus is optional:
If a setter method such as configConfMo is invoked and the ModificationStatus
is not set, the system automatically determines if the object should be created or modified.
|
|
xmitDelay
Type: ospf:XmitDelay
Primitive Type: scalar:Uint16
Like: ospf:AIf:xmitDelay
Units: sec
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The delay time needed to send an LSA update packet. OSPF increments the LSA age time by the transmit delay amount before transmitting the LSA update. You should take into account the transmission and propagation delays for the interface when you set this value.
| |
| Constants |
| defaultValue |
1 |
--- |
NO COMMENTS
|
|