![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:AEPg A set of requirements for the application-level EPG instance. The policy regulates connectivity and visibility among the end points within the scope of the policy. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:CEp A client endpoint attaching to the network. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:Ep The DHCP Discovered Endpoint. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Ip The IP address of an endpoint. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtFromEpIp A target relation to the IP address of an endpoint. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtToEpIp A target relation to the IP address of an endpoint. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsCEpToPathEp A source relation to a path endpoint. This is an internal object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsHyper A source relation to the hypervisor that controls and monitors the APIC VMs. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsNic A source relation to an interface. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsVm A source relation to a virtual machine connected to a hypervisor. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtDestToVPort A target relation to an endpoint. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtFromEp A target relation to the properties of the client defined endpoint attached to the network. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtFromEpForEpToEpg A target relation to the properties of the client defined endpoint attached to the network. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSrcToVPort A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtToEp A target relation to the properties of the client defined endpoint attached to the network. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtToEpForEpToEp A target relation to the properties of the client defined endpoint attached to the network. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtToEpForEpgToEp A target relation to the properties of the client-defined endpoint attached to the network. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtTrEpDst A target relation to the properties of the client-defined endpoint attached to the network. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtTrEpSrc A target relation to the properties of the client-defined endpoint attached to the network. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ProtoAttr The Layer 4 protocol attributes in the criterion. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ProtoAttr The Layer 4 protocol attributes in the criterion. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:VmAttr The virtual attributes in the criterion. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:VmAttr The virtual attributes in the criterion. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:OrchsInfo The orchestration information is used to store orchestration specific properties such as Microsoft Azure Pack. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:QinqFabEncap In the case of EPG to Port assciation with double encap, since there is no concept of qinq pool
and still we support more than one qinq FD,we need to a get a unique fabencap per FD and not per EPG
(if we give one Fabencap for all the FDs under that EPG) Ep learning will break and the vpc sync will break)
So this is the MO which keeps track of the all the double encaps under a given EPG and which acts like a re... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsAEPgMonPol A source relation to the monitoring policy model for the endpoint group semantic scope. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsBd A source relation to the bridge domain associated to this endpoint group. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsCons The Consumer contract profile information. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsLbl A label used by consumers to filter the providers. The label can be parented as follows:
By the consumer endpoint group.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract.
By the relation between the contract interface and contract.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract interface.
A consumer with no label will consume from all the providers of the contract with no labels. A consumer with a specific label... |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsSubjLbl A consumer subject label. In general, a subject label is used as a classification criteria for subjects being consumed/provided by the endpoint groups (EPGs) participating in the contract. The label identifies a subject being consumed by a consumer. It can be parented by 2 different methods. The first method is the relation between the consumer EPG and the contract that is used for filtering the subjects. A label should match either the subject n... |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsConsIf A contract for which the EPG will be a consumer. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsLbl A label used by consumers to filter the providers. The label can be parented as follows:
By the consumer endpoint group.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract.
By the relation between the contract interface and contract.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract interface.
A consumer with no label will consume from all the providers of the contract with no labels. A consumer with a specific label... |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsSubjLbl A consumer subject label. In general, a subject label is used as a classification criteria for subjects being consumed/provided by the endpoint groups (EPGs) participating in the contract. The label identifies a subject being consumed by a consumer. It can be parented by 2 different methods. The first method is the relation between the consumer EPG and the contract that is used for filtering the subjects. A label should match either the subject n... |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsCustQosPol A source relation to a custom QoS policy that enables different levels of service to be assigned to network traffic, including specifications for the Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) value(s) and the 802.1p Dot1p priority. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsDomAtt An EPG can be linked to a domain profile via the Associated Domain Profiles. The domain profiles attached can be VMM, Physical, L2 External, or L3 External Domains. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsFcPathAtt this object is used for creation of static association
with a Path for fcoe. Existence of this implies that the
corresponding set of policies will be resolved into the
node to which the relationship points. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsIntraEpg Intra EPg contract:
Represents that the EPg is moving from "allow all within epg" mode
to a "deny all within epg" mode.
The only type of traffic allowed between EPs in this EPg is the one
specified by contracts EPg associates to with this relation.
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsNodeAtt The static association with an access group is a bundled or unbundled group of ports. The existence of this object implies that the corresponding set of policies will be resolved into the node to which the relationship points. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsPathAtt A source relation to an abstraction of a path endpoint. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsProtBy The taboo contract for which the EPG will be a provider and consumer. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsProv A contract for which the EPG will be a provider. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ProvLbl A label used by a provider for specifying its identity. The parent can be either the provider endpoint group or the relation between the provider endpoint group and a contract. A consumer with no label will consume from all the providers of the contract regardless of the provider label. A consumer with a specific label can only consume from providers matching the label. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ProvSubjLbl A subject label is used as classification criteria for subjects being consumed/provided by the endpoint groups (EPGs) participating in the contract. The label identifies a subject being provided by a provider. It can be parented by 2 different methods. The first method is the relation between the provider EPG and the contract that is used for filtering the subjects. A label should match either the subject name or the label present under the subje... |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsProvDef A source relation to a binary contract profile. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsSecInherited Represents that the EPg is inheriting security configuration from another EPg |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtARemoteHostToEpg A target relation to teh abstract representation of the resolvable endpoint profile. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtDestEpg A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtDevEpg A target relation to an endpoint. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtEpg A target relation to an attachable target group. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtExtdevMgrMgmtEPg Association to the Management EPg for this Controller
@@@ This is used to decide the Context (VRF) in which
@@@ the controller is present.
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtFromEpg A target relation to a set of requirements for the application-level endpoint group instance. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtFuncToEpg A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtInstPToNatMappingEPg Relation to the EPg that traffic should
traverse if NAT is required.
Currently used only by OVS in OpenStack envs. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtMgmtEPg A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtNtpProvToEpg A target relation to an attachable target group. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtPoeEpg Represents the EPg the interface policy uses |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtProv A target relation to a set of requirements for the application-level endpoint group instance. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtRtdEpPToNatMappingEPg Relation to the EPg that traffic should
traverse if NAT is required.
Currently used only by OVS in OpenStack envs. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSecInherited Represents that the EPg is inheriting security configuration from another EPg |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSecProvToEpg A target relation to an attachable target group. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSrcToEpg A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSvcMgmtEpg A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSvrToMgmtEPg Association to the Management EPg for this Svr
@@@ This is used to decide the Context (VRF) in which
@@@ the Svr is present.
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtTermToEPg A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtToEpg A target relation to a set of requirements for the application-level endpoint group instance. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtToEpgForEpgToEpg A target relation to a set of requirements for the application-level endpoint group instance. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtVConnToEpgEp A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtVsrcToEpg A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:SharedService When an EPG contains this object, its pcTag is allocated from Shared. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:CtxSharedServiceUpdate An object to trigger Ctx update tasks
@@@ If InstP is in shared service mode and it has
@@@ 0/0 Subnet, its VRF must have a global pcTag
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:CreatedBy A container that captures information about the creator of an object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:StCEp The static endpoint represents a silent client attached to the fabric which will not produce traffic of its own. The configuration of a static endpoint will prevent the client from aging out of relevant addressing tables. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsStCEpToPathEp A source relation to the abstraction of a path endpoint. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:StIp The static client endpoint IP address. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:Subnet A subnet defines the IP address range that can be used within the bridge domain. While a context defines a unique layer 3 space, that space can consist of multiple subnets. These subnets are defined per bridge domain. A bridge domain can contain multiple subnets, but a subnet is contained within a single bridge domain. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:CepNetCfgPol Represents Client End Point network configuration policy,
Used this information for Microsoft SCVMM/Azure application
to create SCVMM static IP pool |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsBDSubnetToProfile The external networks that are routed via Layer 3 networks outside the fabric that are reachable by a tenant's applications. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:UpdateContract If EPg pcTag gets allocated in postExplicit, there might be a race condition
since contract updates happens in postExplicit as well (which might cause
contract shard to be updated with wrong pcTag)
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:NodeInst The health score instance calculated on a node and reported to appliance. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
orchs:LDevVipCfg This is used to store orchestration specific properties like Microsoft Azure Pack |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:ACCfg Contains a hierarchy of folders and parameters similar to AMItem. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RsCfgToConn A source relation to a connector. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RsCfgToVConn A source relation to a virtual connector. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fvns:UcastAddrBlk Defines the first and last unicast IP addresses in the namespace block. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:CtrlrEp The controller appliance IP address and connectivity information. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RtVnsCtrlrEp A target relation to the controller appliance IP address and connectivity information. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RsCfgToConn A source relation to a connector. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RsCfgToVConn A source relation to a virtual connector. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:ParamInst A parameter instance configured by the administrator. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RsCfgToConn A source relation to a connector. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RsCfgToVConn A source relation to a virtual connector. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RsCfgToConn A source relation to a connector. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RsCfgToVConn A source relation to a virtual connector. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RsScopeToTerm A source relation to contract terminal node for parameter resolution. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vns:RtFolderInstAtt A target relation to a folder instance configured by the administrator. Note that this relation is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsCtrctLbl A consumer contract label. A contract label can be parented by the relation between an endpoint group (EPG) and security group. The EPG is associated with a group and lists all contracts it provides out of the group, as well as, optionally, contracts that it chooses to consume. If no consumption contracts are indicated, all contracts are consumed. If no provider contracts are identified, the EPG provides no contracts out of this group. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsLbl A label used by consumers to filter the providers. The label can be parented as follows:
By the consumer endpoint group.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract.
By the relation between the contract interface and contract.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract interface.
A consumer with no label will consume from all the providers of the contract with no labels. A consumer with a specific label... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsSubjLbl A consumer subject label. In general, a subject label is used as a classification criteria for subjects being consumed/provided by the endpoint groups (EPGs) participating in the contract. The label identifies a subject being consumed by a consumer. It can be parented by 2 different methods. The first method is the relation between the consumer EPG and the contract that is used for filtering the subjects. A label should match either the subject n... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ProvCtrctLbl A label identifying a contract. A contract label can be parented by the relation between an endpoint group (EPG) and security group. The EPG is associated with a group and lists all contracts it provides out of the group, as well as, optionally, contracts that it chooses to consume. If no consumption contracts are indicated, all contracts are consumed. If no provider contracts are identified, the EPG provides no contracts out of this group. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ProvLbl A label used by a provider for specifying its identity. The parent can be either the provider endpoint group or the relation between the provider endpoint group and a contract. A consumer with no label will consume from all the providers of the contract regardless of the provider label. A consumer with a specific label can only consume from providers matching the label. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ProvSubjLbl A subject label is used as classification criteria for subjects being consumed/provided by the endpoint groups (EPGs) participating in the contract. The label identifies a subject being provided by a provider. It can be parented by 2 different methods. The first method is the relation between the provider EPG and the contract that is used for filtering the subjects. A label should match either the subject name or the label present under the subje... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
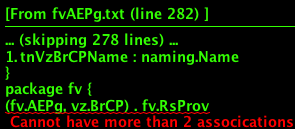
![[V]](styles/eye.gif)