![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
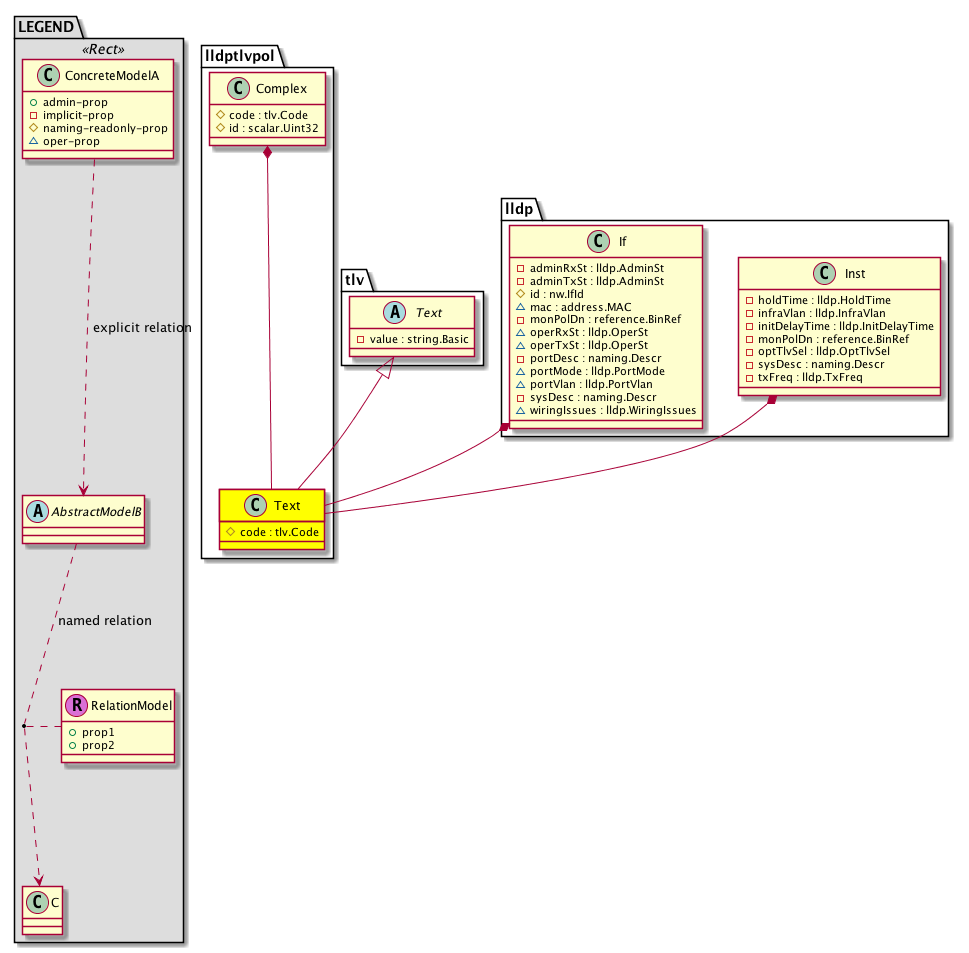
lldp:Entity LLDP allows network devices to advertise information about themselves to other devices on the network. This protocol runs over the data-link layer, which allows two systems running different network layer protocols to learn about each other. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Inst Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) supports a set of attributes that it uses to discover neighbor devices. These attributes contain type, length, and value descriptions and are referred to as TLVs. LLDP supported devices can use TLVs to receive and send information to their neighbors. Details such as configuration information, device capabilities, and device identity can be advertised using this protocol. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldptlvpol:Text A text type, length, value (TLV). |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Entity LLDP allows network devices to advertise information about themselves to other devices on the network. This protocol runs over the data-link layer, which allows two systems running different network layer protocols to learn about each other. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Inst Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) supports a set of attributes that it uses to discover neighbor devices. These attributes contain type, length, and value descriptions and are referred to as TLVs. LLDP supported devices can use TLVs to receive and send information to their neighbors. Details such as configuration information, device capabilities, and device identity can be advertised using this protocol. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldptlvpol:Text A text type, length, value (TLV). |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Entity LLDP allows network devices to advertise information about themselves to other devices on the network. This protocol runs over the data-link layer, which allows two systems running different network layer protocols to learn about each other. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Inst Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) supports a set of attributes that it uses to discover neighbor devices. These attributes contain type, length, and value descriptions and are referred to as TLVs. LLDP supported devices can use TLVs to receive and send information to their neighbors. Details such as configuration information, device capabilities, and device identity can be advertised using this protocol. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:If The LLDP interface, which holds the operational states. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldptlvpol:Text A text type, length, value (TLV). |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Entity LLDP allows network devices to advertise information about themselves to other devices on the network. This protocol runs over the data-link layer, which allows two systems running different network layer protocols to learn about each other. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Inst Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) supports a set of attributes that it uses to discover neighbor devices. These attributes contain type, length, and value descriptions and are referred to as TLVs. LLDP supported devices can use TLVs to receive and send information to their neighbors. Details such as configuration information, device capabilities, and device identity can be advertised using this protocol. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:If The LLDP interface, which holds the operational states. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldptlvpol:Text A text type, length, value (TLV). |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Entity LLDP allows network devices to advertise information about themselves to other devices on the network. This protocol runs over the data-link layer, which allows two systems running different network layer protocols to learn about each other. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Inst Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) supports a set of attributes that it uses to discover neighbor devices. These attributes contain type, length, and value descriptions and are referred to as TLVs. LLDP supported devices can use TLVs to receive and send information to their neighbors. Details such as configuration information, device capabilities, and device identity can be advertised using this protocol. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldptlvpol:Text A text type, length, value (TLV). |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Entity LLDP allows network devices to advertise information about themselves to other devices on the network. This protocol runs over the data-link layer, which allows two systems running different network layer protocols to learn about each other. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Inst Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) supports a set of attributes that it uses to discover neighbor devices. These attributes contain type, length, and value descriptions and are referred to as TLVs. LLDP supported devices can use TLVs to receive and send information to their neighbors. Details such as configuration information, device capabilities, and device identity can be advertised using this protocol. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldptlvpol:Text A text type, length, value (TLV). |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Entity LLDP allows network devices to advertise information about themselves to other devices on the network. This protocol runs over the data-link layer, which allows two systems running different network layer protocols to learn about each other. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Inst Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) supports a set of attributes that it uses to discover neighbor devices. These attributes contain type, length, and value descriptions and are referred to as TLVs. LLDP supported devices can use TLVs to receive and send information to their neighbors. Details such as configuration information, device capabilities, and device identity can be advertised using this protocol. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:If The LLDP interface, which holds the operational states. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldptlvpol:Text A text type, length, value (TLV). |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Entity LLDP allows network devices to advertise information about themselves to other devices on the network. This protocol runs over the data-link layer, which allows two systems running different network layer protocols to learn about each other. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:Inst Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) supports a set of attributes that it uses to discover neighbor devices. These attributes contain type, length, and value descriptions and are referred to as TLVs. LLDP supported devices can use TLVs to receive and send information to their neighbors. Details such as configuration information, device capabilities, and device identity can be advertised using this protocol. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldp:If The LLDP interface, which holds the operational states. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
lldptlvpol:Text A text type, length, value (TLV). |
|