![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
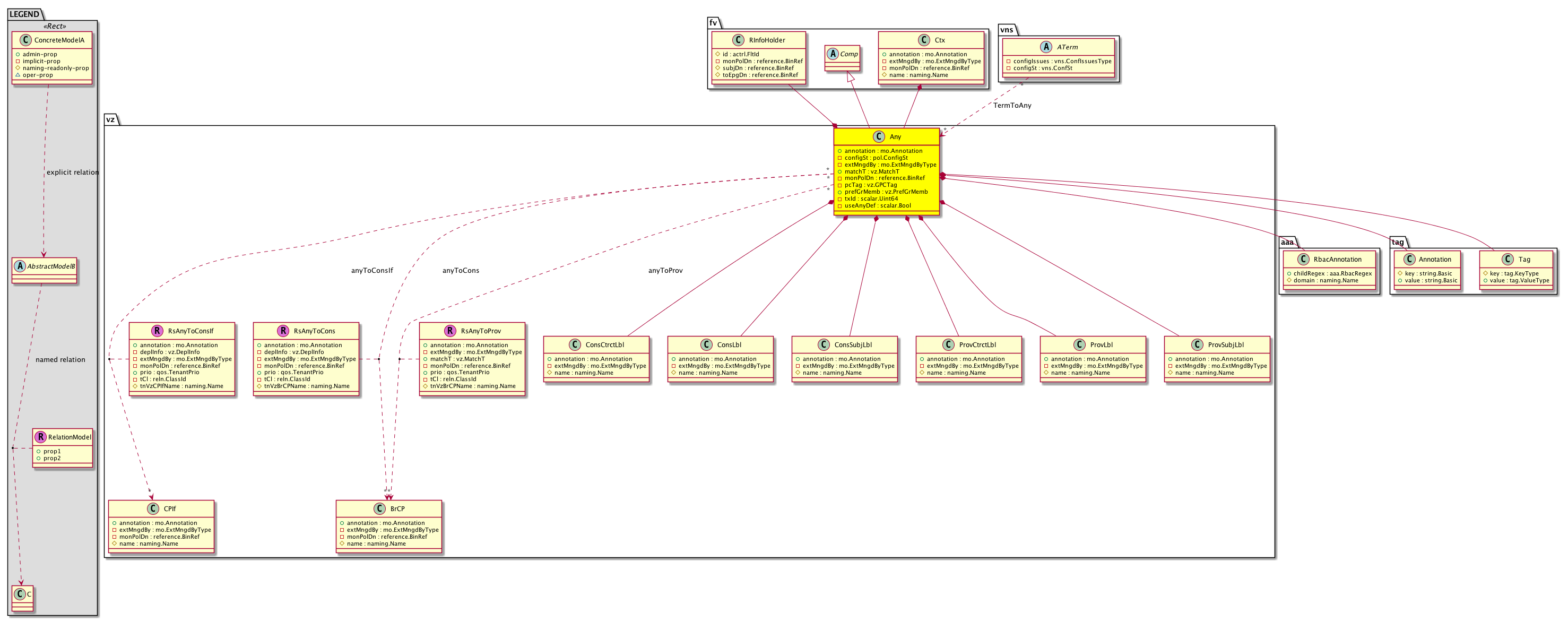
vz:Any vzAny associates all endpoint groups (EPGs) in a context (fvCtx) to one or more contracts (vzBrCP), rather than creating a separate contract relation for each EPG. EPGs can only communicate with other EPGs according to contract rules. A relationship between an EPG and a contract specifies whether the EPG provides the communications defined by the contract rules, consumes them, or both. By dynamically applying contract rules to all EPGs in a conte... |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsCtrctLbl A consumer contract label. A contract label can be parented by the relation between an endpoint group (EPG) and security group. The EPG is associated with a group and lists all contracts it provides out of the group, as well as, optionally, contracts that it chooses to consume. If no consumption contracts are indicated, all contracts are consumed. If no provider contracts are identified, the EPG provides no contracts out of this group. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsLbl A label used by consumers to filter the providers. The label can be parented as follows:
By the consumer endpoint group.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract.
By the relation between the contract interface and contract.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract interface.
A consumer with no label will consume from all the providers of the contract with no labels. A consumer with a specific label... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsSubjLbl A consumer subject label. In general, a subject label is used as a classification criteria for subjects being consumed/provided by the endpoint groups (EPGs) participating in the contract. The label identifies a subject being consumed by a consumer. It can be parented by 2 different methods. The first method is the relation between the consumer EPG and the contract that is used for filtering the subjects. A label should match either the subject n... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ProvCtrctLbl A label identifying a contract. A contract label can be parented by the relation between an endpoint group (EPG) and security group. The EPG is associated with a group and lists all contracts it provides out of the group, as well as, optionally, contracts that it chooses to consume. If no consumption contracts are indicated, all contracts are consumed. If no provider contracts are identified, the EPG provides no contracts out of this group. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ProvLbl A label used by a provider for specifying its identity. The parent can be either the provider endpoint group or the relation between the provider endpoint group and a contract. A consumer with no label will consume from all the providers of the contract regardless of the provider label. A consumer with a specific label can only consume from providers matching the label. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ProvSubjLbl A subject label is used as classification criteria for subjects being consumed/provided by the endpoint groups (EPGs) participating in the contract. The label identifies a subject being provided by a provider. It can be parented by 2 different methods. The first method is the relation between the provider EPG and the contract that is used for filtering the subjects. A label should match either the subject name or the label present under the subje... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsLbl A label used by consumers to filter the providers. The label can be parented as follows:
By the consumer endpoint group.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract.
By the relation between the contract interface and contract.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract interface.
A consumer with no label will consume from all the providers of the contract with no labels. A consumer with a specific label... |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsSubjLbl A consumer subject label. In general, a subject label is used as a classification criteria for subjects being consumed/provided by the endpoint groups (EPGs) participating in the contract. The label identifies a subject being consumed by a consumer. It can be parented by 2 different methods. The first method is the relation between the consumer EPG and the contract that is used for filtering the subjects. A label should match either the subject n... |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:RsAnyToConsIf A source relation to a contract interface. A contract interface can be used as a contract consumption interface when a consumer consumes the contract by associating it to a consumption interface provided by the provider in the consumer's domain. A consumer can associate with the contract consumption interface when it is provided by the provider in the consumer's domain. Note that a contract consumption interface represents one or more subjects de... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsLbl A label used by consumers to filter the providers. The label can be parented as follows:
By the consumer endpoint group.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract.
By the relation between the contract interface and contract.
By the relation between the consumer endpoint group and contract interface.
A consumer with no label will consume from all the providers of the contract with no labels. A consumer with a specific label... |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ConsSubjLbl A consumer subject label. In general, a subject label is used as a classification criteria for subjects being consumed/provided by the endpoint groups (EPGs) participating in the contract. The label identifies a subject being consumed by a consumer. It can be parented by 2 different methods. The first method is the relation between the consumer EPG and the contract that is used for filtering the subjects. A label should match either the subject n... |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ProvLbl A label used by a provider for specifying its identity. The parent can be either the provider endpoint group or the relation between the provider endpoint group and a contract. A consumer with no label will consume from all the providers of the contract regardless of the provider label. A consumer with a specific label can only consume from providers matching the label. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
vz:ProvSubjLbl A subject label is used as classification criteria for subjects being consumed/provided by the endpoint groups (EPGs) participating in the contract. The label identifies a subject being provided by a provider. It can be parented by 2 different methods. The first method is the relation between the provider EPG and the contract that is used for filtering the subjects. A label should match either the subject name or the label present under the subje... |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif)