![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
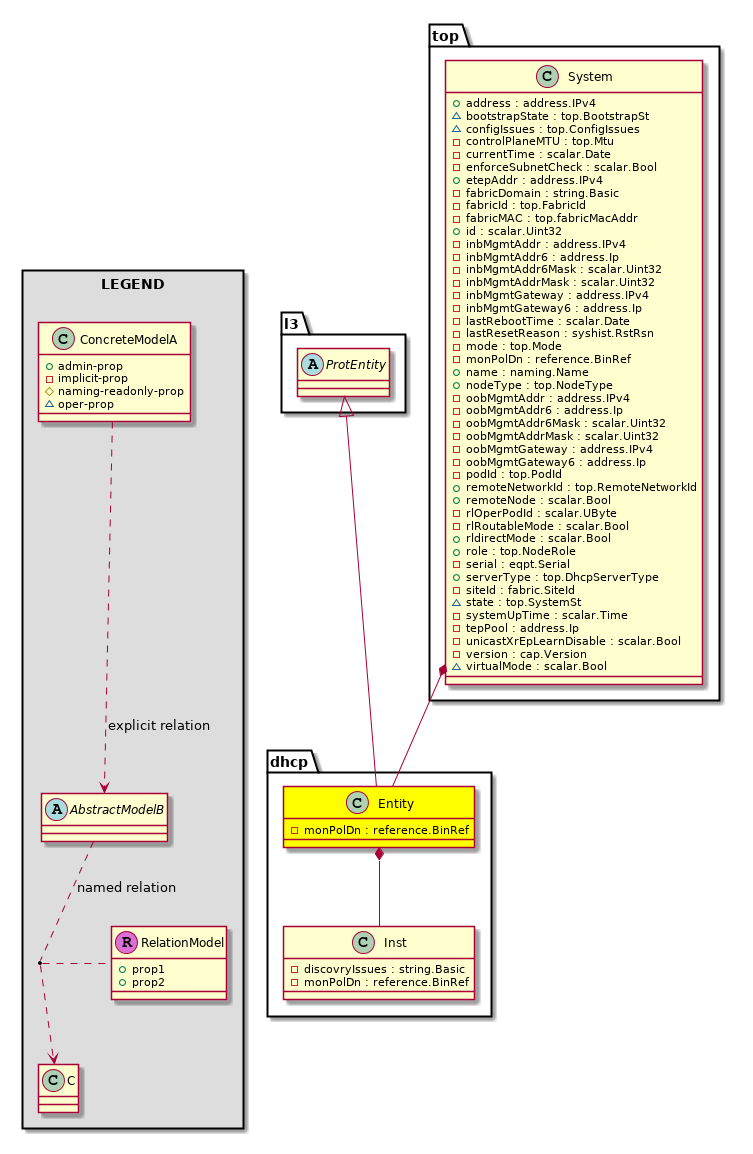
dhcp:Entity Holds DHCP control plane entity information. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:Inst The DHCP instance information. There is only one instance of DHCP relay currently running in the system. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:ClientIf Used for showing client functionality on the interface. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:Complex The Complex type, length, and value (TLV), which contains basic TLVs. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:Ip The IP type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:UByte The 8-bit unsigned integer (UByte) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:UInt16 The 16-bit unsigned integer (UInt16) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:UInt32 The 32-bit unsigned integer (UInt32) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:UInt64 The 64-bit unsigned integer (UInt64) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:Ip The IP type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:UByte The 8-bit unsigned integer (UByte) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:UInt16 The 16-bit unsigned integer (UInt16) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:UInt32 The 32-bit unsigned integer (UInt32) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlv:UInt64 The 64-bit unsigned integer (UInt64) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UByte The 8-bit unsigned integer (UByte) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt16 The 16-bit unsigned integer (UInt16) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt32 The 32-bit unsigned integer (UInt32) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt64 The 64-bit unsigned integer (UInt64) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UByte The 8-bit unsigned integer (UByte) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt16 The 16-bit unsigned integer (UInt16) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt32 The 32-bit unsigned integer (UInt32) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt64 The 64-bit unsigned integer (UInt64) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:RsPseudoIf A source relation to the abstract layer 3 interface. If the mode is pseudo interface, the list of all interfaces that the dhcp requests is flooded. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UByte The 8-bit unsigned integer (UByte) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt16 The 16-bit unsigned integer (UInt16) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt32 The 32-bit unsigned integer (UInt32) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt64 The 64-bit unsigned integer (UInt64) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UByte The 8-bit unsigned integer (UByte) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt16 The 16-bit unsigned integer (UInt16) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt32 The 32-bit unsigned integer (UInt32) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt64 The 64-bit unsigned integer (UInt64) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:RelayIf DHCP relay if used for representing relay functionality on the interface. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:OptionDef The option definition. Each DHCP option is defined by a unique name, ID, and option data. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UByte The 8-bit unsigned integer (UByte) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt16 The 16-bit unsigned integer (UInt16) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt32 The 32-bit unsigned integer (UInt32) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt64 The 64-bit unsigned integer (UInt64) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UByte The 8-bit unsigned integer (UByte) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt16 The 16-bit unsigned integer (UInt16) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt32 The 32-bit unsigned integer (UInt32) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt64 The 64-bit unsigned integer (UInt64) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcp:ServerIf DHCP server if not supported; defined for completeness. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UByte The 8-bit unsigned integer (UByte) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt16 The 16-bit unsigned integer (UInt16) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt32 The 32-bit unsigned integer (UInt32) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt64 The 64-bit unsigned integer (UInt64) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UByte The 8-bit unsigned integer (UByte) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt16 The 16-bit unsigned integer (UInt16) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt32 The 32-bit unsigned integer (UInt32) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
dhcptlvpol:UInt64 The 64-bit unsigned integer (UInt64) type, length, and value (TLV). |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|