![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
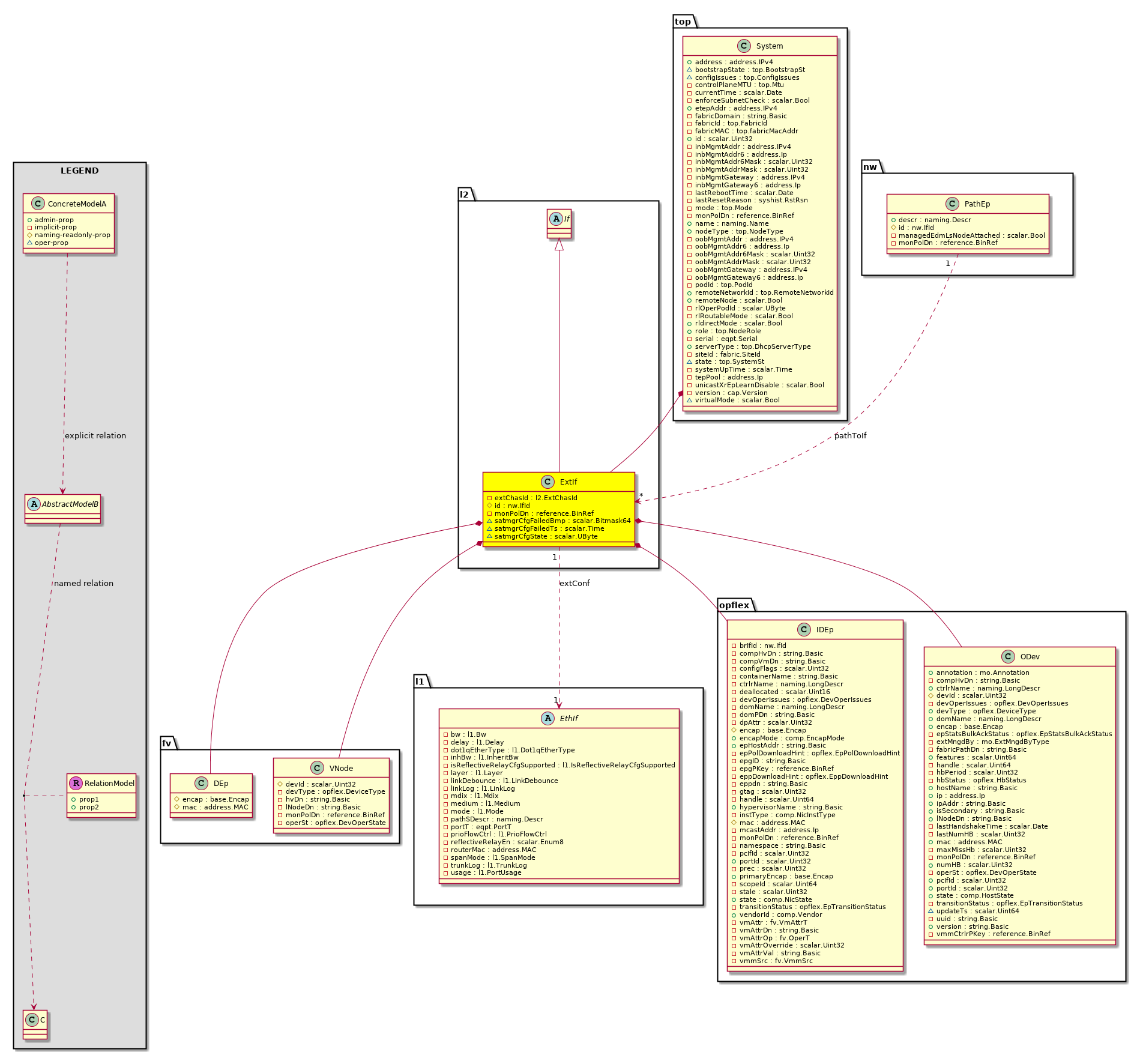
l2:ExtIf The FEX fabric interface. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:DEp A dynamically-learned endpoint on the switch. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsHyper A source relation to the hypervisor that controls and monitors the APIC VMs. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtDestToVPort A target relation to an endpoint. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSrcToVPort A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:VNode An opflex-capable virtual node that is connected to the fabric. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsLNode A source relation to the logical node. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsOpflexHv Relation to the hypervisor in the IFC
for UI display purposes.
Use the new realtion VNodeToHv.
This exists for backward compatibility.
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsVNodeToHv Relation to the hypervisor in the IFC
for UI display purposes
This is needed for stats as multiple ODevs can
point to the same Hv.
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtVNode A target relation to the VNode that contains the endpoint. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l2:RsExtConf A source relation to an L1 interface. This is an internal object |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
opflex:IDEp This is generated and used only by internal processes. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:IDEpToEpDefRef IDEpToEpDefRef represents an object that links IDEp
to corresponding EpDef |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsHyper A source relation to the hypervisor that controls and monitors the APIC VMs. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtDestToVPort A target relation to an endpoint. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSrcToVPort A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:VDEp A virtual datacenter endpoint. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsHyper A source relation to the hypervisor that controls and monitors the APIC VMs. This is an internal object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsVNode A source relation to an opflex-capable virtual node that is connected to the fabric. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtDestToVPort A target relation to an endpoint. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSrcToVPort A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:VDEp A virtual datacenter endpoint. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsHyper A source relation to the hypervisor that controls and monitors the APIC VMs. This is an internal object. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsVNode A source relation to an opflex-capable virtual node that is connected to the fabric. This is an internal object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtDestToVPort A target relation to an endpoint. This is an internal object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSrcToVPort A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:VDEp A virtual datacenter endpoint. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsHyper A source relation to the hypervisor that controls and monitors the APIC VMs. This is an internal object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:ReportingNode The node reporting a corresponding endpoint. This enables a user to see on which nodes the endpoints are present. This is an internally created object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsVNode A source relation to an opflex-capable virtual node that is connected to the fabric. This is an internal object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtDestToVPort A target relation to an endpoint. This is an internal object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtSrcToVPort A target relation to a set of endpoints. This is an internal object. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
opflex:ODev This is generated and used only by internal processes. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:VNode An opflex-capable virtual node that is connected to the fabric. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsLNode A source relation to the logical node. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsOpflexHv Relation to the hypervisor in the IFC
for UI display purposes.
Use the new realtion VNodeToHv.
This exists for backward compatibility.
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RsVNodeToHv Relation to the hypervisor in the IFC
for UI display purposes
This is needed for stats as multiple ODevs can
point to the same Hv.
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:RtVNode A target relation to the VNode that contains the endpoint. This is an internal object. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
opflex:ODevCap This is generated and used only by internal processes. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|