![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
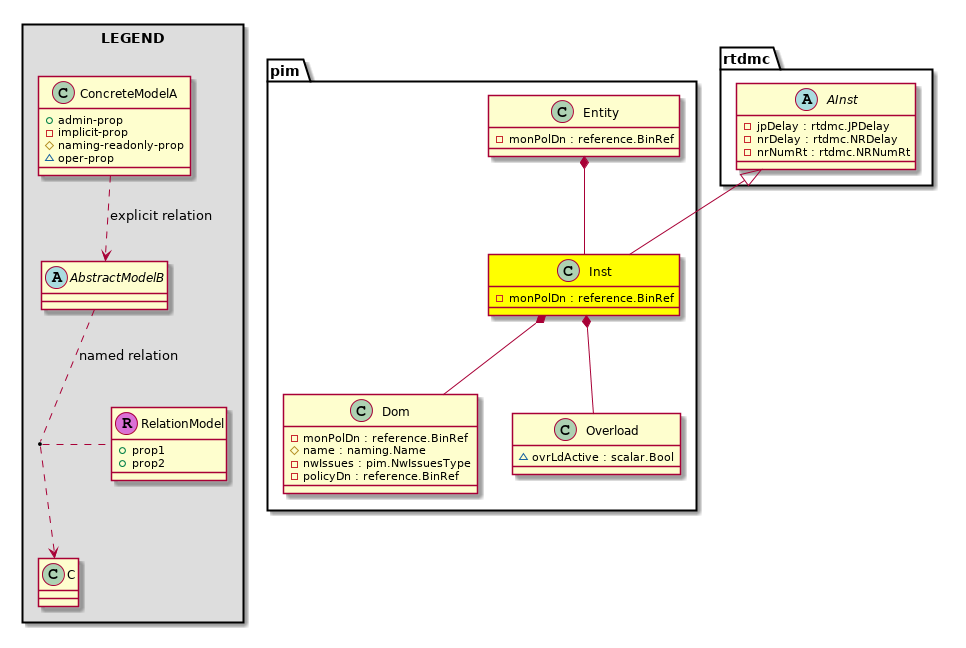
pim:Inst PIM instance information. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pim:Dom PIM domain (VRF) information. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pim:SGRangeExpP This object holds (S,G) expiry timer policy for specified range |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pim:AcastRPFuncP The Anycast RP function policy. Specifies the Anycast and local interface for the Anycast RP and all the peer's local info. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pim:MAFuncP Auto-RP mapping agent (MA) function policy. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pim:BSRP The Bootstrap Router (BSR) policy. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pim:If PIM interface information. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pim:IfStats This object holds the pim interface related statistics |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pim:ResP Resource (router state) limit policy. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
pim:StaticRP Static RP information. If the RP address is configured locally, the router assumes RP functionality. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|