![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
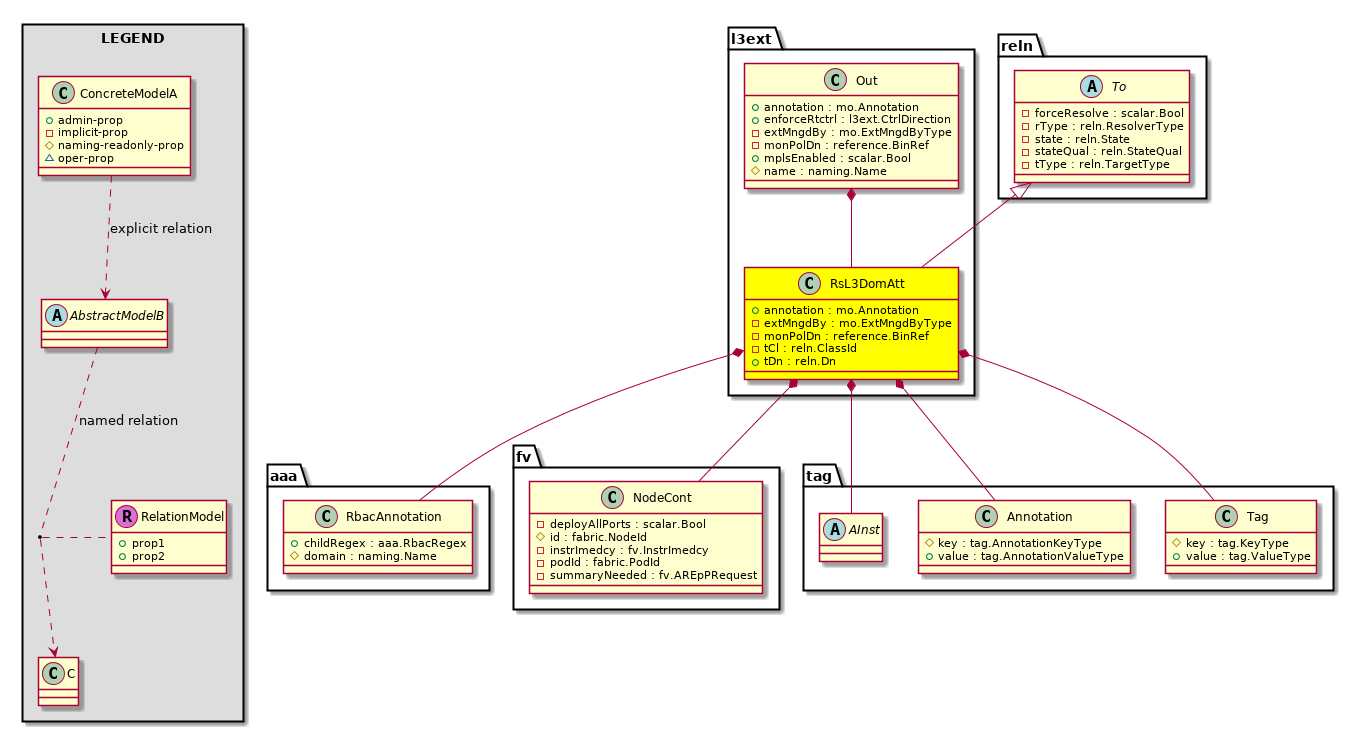
l3ext:RsL3DomAtt A source relation to the outside domain advertising these prefixes and relationship to the L2 domain for external SWI. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Counts An immutable object that provides the number of critical, major, minor, and warning faults raised on its parent object and its subtree. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Inst Contains detailed information of a fault. This object is attached as a child of the object on which the fault condition occurred. One instance object is created for each fault
condition of the parent object. A fault instance object is identified by a fault code. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EncapDef An internal encapsulation definition. This is an internal object used for deployment of encapsulation. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
igmp:SnoopAccessGroupDef In case the filter will take place at the fvAEPg level For future releases Internal Representation of an IGMP snooping filter |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
igmp:SnoopStaticGroupDef In case the static group membership is at the
fvAEPg level For future releases Internal representation of the group memebership |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
mld:SnoopAccessGroupDef In case the filter will take place at the fvAEPg level For future releases Internal Representation of an MLD snooping filter |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
mld:SnoopStaticGroupDef In case the static group membership is at the
fvAEPg level For future releases Internal representation of the group memebership |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ptp:CfgDef PTP internal representation for ptp Cfg |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
ptp:UcastIp This object holds unicast ip address information |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
aaa:RbacAnnotation RbacAnnotation is used for capturing rbac properties of any apic object
Objects can append rbacannotations as Object->RbacAnnotation which
is then checked for domain eligibility |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fv:EncapDef An internal encapsulation definition. This is an internal object used for deployment of encapsulation. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
health:Inst A base class for a health score instance.(Switch only) |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
tag:AInst The label instance, which is contained by the taggable object. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|