| Properties Summary |
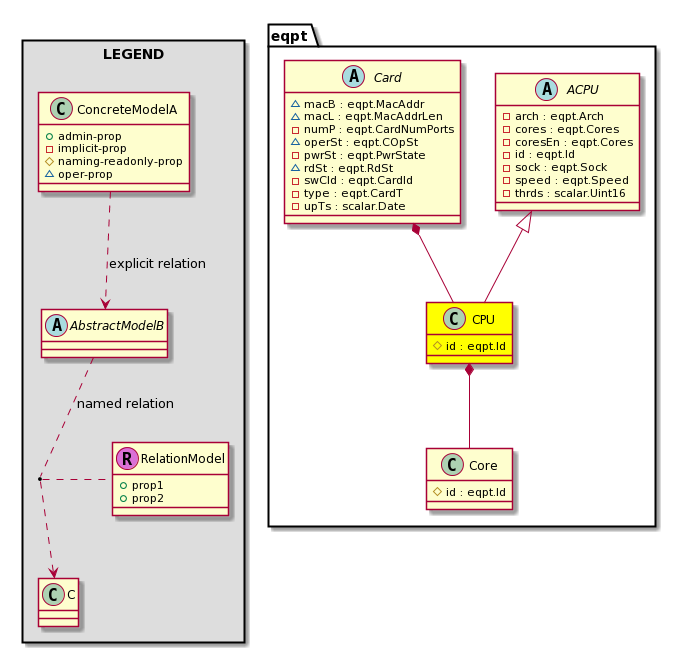
arch
Type: eqpt:Arch
Primitive Type: scalar:Enum8
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The internal architecture of the CPU including features and services.
| |
| Constants |
| any |
0 |
any |
NO COMMENTS
|
| x86_32 |
1 |
x86_32 |
x86 32 bit
|
| x86_64 |
2 |
x86_64 |
x86 64 bit
|
| DEFAULT |
0 |
--- |
CPU Architecture
|
|
childAction
Type: mo:ModificationChildAction
Primitive Type: scalar:Bitmask32
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelChildAction
Comments:
-
Delete or ignore. For internal use only.
| |
| Constants |
| deleteAll |
16384u |
deleteAll |
NO COMMENTS
|
| ignore |
4096u |
ignore |
NO COMMENTS
|
| deleteNonPresent |
8192u |
deleteNonPresent |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
0 |
--- |
This type is used to
|
|
cores
Type: eqpt:Cores
Primitive Type: scalar:Uint16
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The number of processing cores on the CPU.
| |
| Constants |
| unspecified |
0 |
number of cores |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
0 |
--- |
Number of cores
|
|
coresEn
Type: eqpt:Cores
Primitive Type: scalar:Uint16
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The number of enabled processing cores on the CPU.
| |
| Constants |
| unspecified |
0 |
number of cores |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
0 |
--- |
Number of cores
|
|
descr
Type: naming:Descr
Primitive Type: string:Basic
Like: naming:Described:descr
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: admin
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
Additional descriptive information about the object.
dn
Type: reference:BinRef
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelDn
Comments:
-
A tag or metadata is a non-hierarchical keyword or term assigned to the fabric module.
id
Type: eqpt:Id
Primitive Type: scalar:Uint32
Overrides:eqpt:ACPU:id | eqpt:Item:id
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Naming Property -- [NAMING RULES]
Access: naming
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The CPU ID.
mfgTm
Type: scalar:Date
Like: eqpt:Mfg:mfgTm
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The manufacturing time.
| |
| Constants |
| not-applicable |
0ull |
N/A |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
not-applicable(0ull) |
N/A |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
modTs
Type: mo:TStamp
Primitive Type: scalar:Date
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The time when this object was last modified.
| |
| Constants |
| never |
0ull |
never |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
never(0ull) |
never |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
model
Type: eqpt:Model
Primitive Type: string:Basic
Like: eqpt:Dev:model
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The model of the component.
rev
Type: eqpt:Revision
Primitive Type: string:Basic
Like: eqpt:Dev:rev
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The revision number.
| |
| Constants |
| defaultValue |
"0" |
--- |
NO COMMENTS
|
|
rn
Type: reference:BinRN
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRn
Comments:
-
Identifies an object from its siblings within the context of its parent object. The distinguished name contains a sequence of relative names.
ser
Type: eqpt:Serial
Primitive Type: string:Basic
Like: eqpt:Dev:ser
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The serial number.
sock
Type: eqpt:Sock
Primitive Type: scalar:Enum8
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The CPU socket designation.
| |
| Constants |
| unspecified |
0 |
socket |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
0 |
--- |
Socket
|
|
speed
Type: eqpt:Speed
Primitive Type: scalar:Float
Units: GHz
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The CPU speed.
| |
| Constants |
| unspecified |
0 |
speed |
NO COMMENTS
|
| DEFAULT |
0 |
--- |
Speed
|
|
status
Type: mo:ModificationStatus
Primitive Type: scalar:Bitmask32
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelStatus
Comments:
-
The upgrade status. This property is for internal use only.
| |
| Constants |
| created |
2u |
created |
In a setter method: specifies that an object should be created.
An error is returned if the object already exists.
In the return value of a setter method: indicates that an object has been created.
|
| modified |
4u |
modified |
In a setter method: specifies that an object should be modified
In the return value of a setter method: indicates that an object has been modified.
|
| deleted |
8u |
deleted |
In a setter method: specifies that an object should be deleted.
In the return value of a setter method: indicates that an object has been deleted.
|
| DEFAULT |
0 |
--- |
This type controls the life cycle of objects passed in the XML API.
When used in a setter method (such as configConfMo), the ModificationStatus
specifies whether an object should be created, modified, deleted or removed.
In the return value of a setter method, the ModificationStatus indicates the actual
operation that was performed. For example, the ModificationStatus is set to "created"
if the object was created. The ModificationStatus is not set if the object was neither
created, modified, deleted or removed.
When invoking a setter method, the ModificationStatus is optional:
If a setter method such as configConfMo is invoked and the ModificationStatus
is not set, the system automatically determines if the object should be created or modified.
|
|
thrds
Type: scalar:Uint16
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The number of threads that can be executed in parallel within each CPU.
vendor
Type: eqpt:Vendor
Primitive Type: string:Basic
Like: eqpt:Dev:vendor
Units: null
Encrypted: false
Access: implicit
Category: TopLevelRegular
Comments:
-
The vendor.
| |
| Constants |
| defaultValue |
"Cisco Systems, Inc" |
--- |
NO COMMENTS
|
|