![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
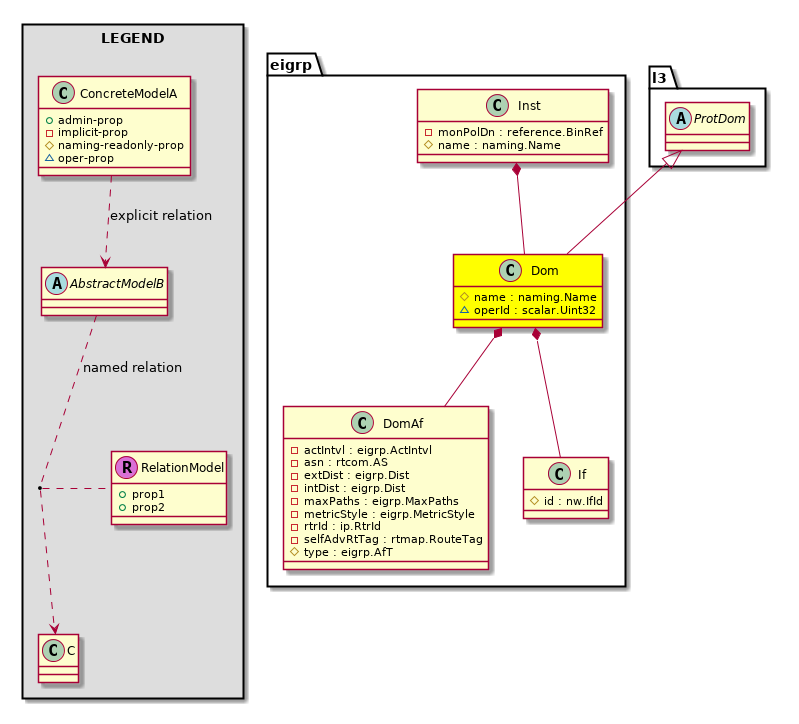
eigrp:Dom The EIGRP domain (VRF) information. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
eigrp:DomAf The EIGRP address family domain (VRF) information. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
eigrp:ExtProtNhRec The EIGRP nexthop information for external routes. External routes are routes from a different protocol or from a different EIGRP AS. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
eigrp:InterLeakP The inter protocol route leak policy, which defines the distribution of routes from one protocol to another. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
eigrp:If An EIGRP configured interface combines the benefits of distance vector protocols with the features of link-state protocols. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
eigrp:AuthP This object holds authentication policy information |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
eigrp:RtCtrlP The route control policy for routes coming/going over interfaces.
There are few ways to apply this policy, controlling
through route maps or prefix lists.
The direction specifies whether to apply this policy
in the incoming or outgoing direction |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
eigrp:RtMetricAlterP Metric Alteration policy for EIGRP routes.
Selection of routes for which metric has to be adjusted,
can be done through route maps or prefix lists.
The direction specifies whether to apply this policy
for incoming or outgoing routes |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
fault:Delegate Exposes internal faults to the user. A fault delegate object can be defined on IFC (for example, for an endpoint group) and when the fault is raised
(for example, under an endpoint policy on a switch), a fault delegate object is created on IFC under the specified object. A fault delegate object follows the lifecycle of the original fault instance object, being created, modified, or deleted based on the changes of the original fault. |
|