![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:CtxSubstitute Tenant context object substitute.
Its needed for internal PE purposes but it doesnt instantiate any
VRF in the node. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
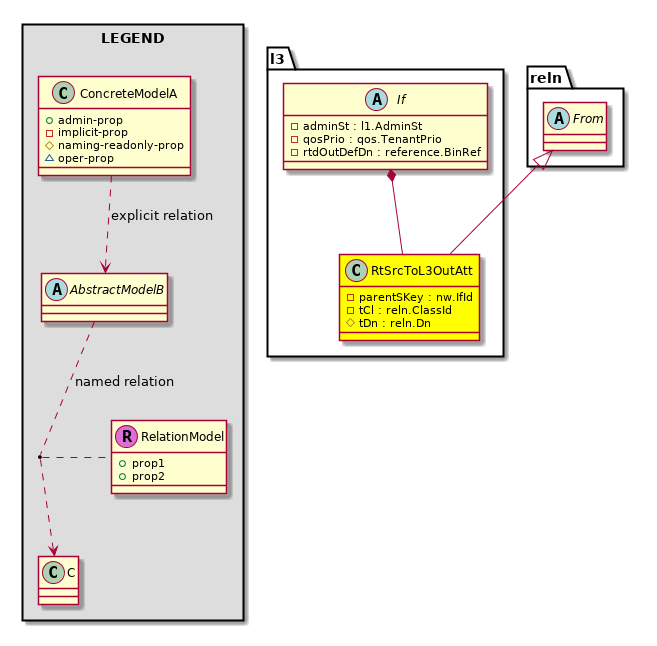
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:CtxSubstitute Tenant context object substitute.
Its needed for internal PE purposes but it doesnt instantiate any
VRF in the node. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Inst The infra VRF is created for the iNXOS fabric infrastructure. All communications between fabric elements, such as spine, leaf and vleaf, take place in this VRF. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Inst The infra VRF is created for the iNXOS fabric infrastructure. All communications between fabric elements, such as spine, leaf and vleaf, take place in this VRF. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Ctx The tenant context information is equivalent to a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance created for the tenant's L3 network. Similar to a VRF in traditional Cisco routers, the tenant context isolates the IP addresses of the tenant, allowing different tenants to have overlapping IP addresses. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Ctx The tenant context information is equivalent to a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance created for the tenant's L3 network. Similar to a VRF in traditional Cisco routers, the tenant context isolates the IP addresses of the tenant, allowing different tenants to have overlapping IP addresses. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:CtxSubstitute Tenant context object substitute.
Its needed for internal PE purposes but it doesnt instantiate any
VRF in the node. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:CtxSubstitute Tenant context object substitute.
Its needed for internal PE purposes but it doesnt instantiate any
VRF in the node. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Inst The infra VRF is created for the iNXOS fabric infrastructure. All communications between fabric elements, such as spine, leaf and vleaf, take place in this VRF. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Inst The infra VRF is created for the iNXOS fabric infrastructure. All communications between fabric elements, such as spine, leaf and vleaf, take place in this VRF. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Ctx The tenant context information is equivalent to a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance created for the tenant's L3 network. Similar to a VRF in traditional Cisco routers, the tenant context isolates the IP addresses of the tenant, allowing different tenants to have overlapping IP addresses. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Ctx The tenant context information is equivalent to a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance created for the tenant's L3 network. Similar to a VRF in traditional Cisco routers, the tenant context isolates the IP addresses of the tenant, allowing different tenants to have overlapping IP addresses. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:CtxSubstitute Tenant context object substitute.
Its needed for internal PE purposes but it doesnt instantiate any
VRF in the node. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:EncRtdIf The routed interface corresponds to a sub-interface in Cisco?s routing terminology. A sub-interface is a logical L3 interface created on an underlying physical L3 port (the parent interface). Each sub-interface is associated with an 802.1Q VLAN tag. The traffic that comes on the parent interface with that tag is considered for that sub-interface.
The existence of a routed interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that the interface belo... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:CtxSubstitute Tenant context object substitute.
Its needed for internal PE purposes but it doesnt instantiate any
VRF in the node. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:EncRtdIf The routed interface corresponds to a sub-interface in Cisco?s routing terminology. A sub-interface is a logical L3 interface created on an underlying physical L3 port (the parent interface). Each sub-interface is associated with an 802.1Q VLAN tag. The traffic that comes on the parent interface with that tag is considered for that sub-interface.
The existence of a routed interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that the interface belo... |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Inst The infra VRF is created for the iNXOS fabric infrastructure. All communications between fabric elements, such as spine, leaf and vleaf, take place in this VRF. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:EncRtdIf The routed interface corresponds to a sub-interface in Cisco?s routing terminology. A sub-interface is a logical L3 interface created on an underlying physical L3 port (the parent interface). Each sub-interface is associated with an 802.1Q VLAN tag. The traffic that comes on the parent interface with that tag is considered for that sub-interface.
The existence of a routed interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that the interface belo... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Inst The infra VRF is created for the iNXOS fabric infrastructure. All communications between fabric elements, such as spine, leaf and vleaf, take place in this VRF. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:EncRtdIf The routed interface corresponds to a sub-interface in Cisco?s routing terminology. A sub-interface is a logical L3 interface created on an underlying physical L3 port (the parent interface). Each sub-interface is associated with an 802.1Q VLAN tag. The traffic that comes on the parent interface with that tag is considered for that sub-interface.
The existence of a routed interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that the interface belo... |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Ctx The tenant context information is equivalent to a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance created for the tenant's L3 network. Similar to a VRF in traditional Cisco routers, the tenant context isolates the IP addresses of the tenant, allowing different tenants to have overlapping IP addresses. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:EncRtdIf The routed interface corresponds to a sub-interface in Cisco?s routing terminology. A sub-interface is a logical L3 interface created on an underlying physical L3 port (the parent interface). Each sub-interface is associated with an 802.1Q VLAN tag. The traffic that comes on the parent interface with that tag is considered for that sub-interface.
The existence of a routed interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that the interface belo... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Ctx The tenant context information is equivalent to a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance created for the tenant's L3 network. Similar to a VRF in traditional Cisco routers, the tenant context isolates the IP addresses of the tenant, allowing different tenants to have overlapping IP addresses. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:EncRtdIf The routed interface corresponds to a sub-interface in Cisco?s routing terminology. A sub-interface is a logical L3 interface created on an underlying physical L3 port (the parent interface). Each sub-interface is associated with an 802.1Q VLAN tag. The traffic that comes on the parent interface with that tag is considered for that sub-interface.
The existence of a routed interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that the interface belo... |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:CtxSubstitute Tenant context object substitute.
Its needed for internal PE purposes but it doesnt instantiate any
VRF in the node. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtdIf A target relation to the routed concrete interface. This corresponds to a physical L3 interface.
The existence of a routed concrete interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that interface belongs to that VRF. An L3 interface can belong to only one VRF at a time. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:CtxSubstitute Tenant context object substitute.
Its needed for internal PE purposes but it doesnt instantiate any
VRF in the node. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtdIf A target relation to the routed concrete interface. This corresponds to a physical L3 interface.
The existence of a routed concrete interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that interface belongs to that VRF. An L3 interface can belong to only one VRF at a time. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Inst The infra VRF is created for the iNXOS fabric infrastructure. All communications between fabric elements, such as spine, leaf and vleaf, take place in this VRF. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtdIf A target relation to the routed concrete interface. This corresponds to a physical L3 interface.
The existence of a routed concrete interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that interface belongs to that VRF. An L3 interface can belong to only one VRF at a time. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Inst The infra VRF is created for the iNXOS fabric infrastructure. All communications between fabric elements, such as spine, leaf and vleaf, take place in this VRF. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtdIf A target relation to the routed concrete interface. This corresponds to a physical L3 interface.
The existence of a routed concrete interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that interface belongs to that VRF. An L3 interface can belong to only one VRF at a time. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Ctx The tenant context information is equivalent to a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance created for the tenant's L3 network. Similar to a VRF in traditional Cisco routers, the tenant context isolates the IP addresses of the tenant, allowing different tenants to have overlapping IP addresses. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtdIf A target relation to the routed concrete interface. This corresponds to a physical L3 interface.
The existence of a routed concrete interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that interface belongs to that VRF. An L3 interface can belong to only one VRF at a time. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Ctx The tenant context information is equivalent to a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance created for the tenant's L3 network. Similar to a VRF in traditional Cisco routers, the tenant context isolates the IP addresses of the tenant, allowing different tenants to have overlapping IP addresses. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtdIf A target relation to the routed concrete interface. This corresponds to a physical L3 interface.
The existence of a routed concrete interface under a VRF or infra VRF also implies that interface belongs to that VRF. An L3 interface can belong to only one VRF at a time. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:CtxSubstitute Tenant context object substitute.
Its needed for internal PE purposes but it doesnt instantiate any
VRF in the node. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l2:BD The Layer 2 Bridge-domain identifies the boundary of a tenant?s bridged/layer 2 traffic. This is similar to a VLAN in a traditional layer 2 switched network. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
svi:If A routed VLAN interface. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:CtxSubstitute Tenant context object substitute.
Its needed for internal PE purposes but it doesnt instantiate any
VRF in the node. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l2:BD The Layer 2 Bridge-domain identifies the boundary of a tenant?s bridged/layer 2 traffic. This is similar to a VLAN in a traditional layer 2 switched network. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
svi:If A routed VLAN interface. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Inst The infra VRF is created for the iNXOS fabric infrastructure. All communications between fabric elements, such as spine, leaf and vleaf, take place in this VRF. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l2:BD The Layer 2 Bridge-domain identifies the boundary of a tenant?s bridged/layer 2 traffic. This is similar to a VLAN in a traditional layer 2 switched network. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
svi:If A routed VLAN interface. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Inst The infra VRF is created for the iNXOS fabric infrastructure. All communications between fabric elements, such as spine, leaf and vleaf, take place in this VRF. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l2:BD The Layer 2 Bridge-domain identifies the boundary of a tenant?s bridged/layer 2 traffic. This is similar to a VLAN in a traditional layer 2 switched network. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
svi:If A routed VLAN interface. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Ctx The tenant context information is equivalent to a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance created for the tenant's L3 network. Similar to a VRF in traditional Cisco routers, the tenant context isolates the IP addresses of the tenant, allowing different tenants to have overlapping IP addresses. |
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l2:BD The Layer 2 Bridge-domain identifies the boundary of a tenant?s bridged/layer 2 traffic. This is similar to a VLAN in a traditional layer 2 switched network. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
svi:If A routed VLAN interface. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:Root This class represents the root element in the object hierarchy.
All managed objects in the system are descendants of the Root element. |
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
top:System The APIC uses a policy model to combine data into a health score. Health scores can be aggregated for a variety of areas such as for the infrastructure, applications, or services. The category health score is calculated using a Lp -Norm formula. The health score penalty equals 100 minus the health score. The health score penalty represents the overall health score penalties of a set of MOs that belong to a given category and are children or direc... |
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:Ctx The tenant context information is equivalent to a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance created for the tenant's L3 network. Similar to a VRF in traditional Cisco routers, the tenant context isolates the IP addresses of the tenant, allowing different tenants to have overlapping IP addresses. |
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l2:BD The Layer 2 Bridge-domain identifies the boundary of a tenant?s bridged/layer 2 traffic. This is similar to a VLAN in a traditional layer 2 switched network. |
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
svi:If A routed VLAN interface. |
|
|
|
|
├
|
![[V]](styles/eye.gif) |
l3:RtSrcToL3OutAtt Relation to the L3 out |
|